An HDAC3-PROX1 corepressor module acts on HNF4α to control hepatic triglycerides
- PMID: 28916805
- PMCID: PMC5601916
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00772-5
An HDAC3-PROX1 corepressor module acts on HNF4α to control hepatic triglycerides
Abstract
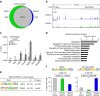
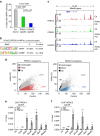
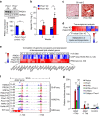
The histone deacetylase HDAC3 is a critical mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism, and liver-specific deletion of HDAC3 leads to fatty liver. To elucidate the underlying mechanism, here we report a method of cross-linking followed by mass spectrometry to define a high-confidence HDAC3 interactome in vivo that includes the canonical NCoR-HDAC3 complex as well as Prospero-related homeobox 1 protein (PROX1). HDAC3 and PROX1 co-localize extensively on the mouse liver genome, and are co-recruited by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α). The HDAC3-PROX1 module controls the expression of a gene program regulating lipid homeostasis, and hepatic-specific ablation of either component increases triglyceride content in liver. These findings underscore the importance of specific combinations of transcription factors and coregulators in the fine tuning of organismal metabolism.HDAC3 is a critical mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism and its loss leads to fatty liver. Here, the authors characterize the liver HDAC3 interactome in vivo, provide evidence that HDAC3 interacts with PROX1, and show that HDAC3 and PROX1 control expression of genes regulating lipid homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
M.A.L. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of KDAC, Eli Lilly and Company, and Pfizer, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

