The effects of different enrofloxacin dosages on clinical efficacy and resistance development in chickens experimentally infected with Salmonella Typhimurium
- PMID: 28916830
- PMCID: PMC5601478
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12294-7
The effects of different enrofloxacin dosages on clinical efficacy and resistance development in chickens experimentally infected with Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
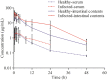
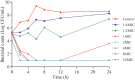
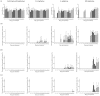
To investigate the optimal dosage which can improve clinical efficacy and minimize resistance, pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics model of enrofloxacin was established. Effect of enrofloxacin treatments on clearance of Salmonella in experimentally infected chickens and simultaneously resistance selection in Salmonella and coliforms were evaluated in three treatment groups (100, PK/PD designed dosage of 4, 0.1 mg/kg b.w.) and a control group. Treatment duration was three rounds of 7-day treatment alternated with 7-day withdrawal. Results showed that 100 mg/kg b.w. of enrofloxacin completely eradicated Salmonella, but resistant coliforms (4.0-60.8%) were selected from the end of the second round's withdrawal period till the end of the experiment (days 28-42). PK/PD based dosage (4 mg/kg b.w.) effectively reduced Salmonella for the first treatment duration. However upon cessation of medication, Salmonella repopulated chickens and persisted till the end with reduced susceptibility (MICCIP = 0.03-0.25 mg/L). Low frequency (5-9.5%) of resistant coliforms was selected (days 39-42). Enrofloxacin at dosage of 0.1 mg/kg b.w. was not able to eliminate Salmonella and selected coliforms with slight decreased susceptibility (MICENR = 0.25 mg/L). In conclusion, short time treatment (7 days) of enrofloxacin at high dosage (100 mg/kg b.w.) could be effective in treating Salmonella infection while minimizing resistance selection in both Salmonella and coliforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
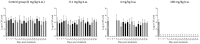
Similar articles
-
Modification of enrofloxacin treatment regimens for poultry experimentally infected with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 to minimize selection of resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Dec;50(12):4030-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00525-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 17030564 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of oral and intramuscular administration and dose escalation of enrofloxacin on the selection of quinolone resistance among Salmonella and coliforms in pigs.Res Vet Sci. 2003 Dec;75(3):185-93. doi: 10.1016/s0034-5288(03)00112-7. Res Vet Sci. 2003. PMID: 13129666
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic integration of enrofloxacin against Salmonella Enteritidis after administering to broiler chicken by per-oral and intravenous routes.J Vet Sci. 2019 Mar;20(2):e15. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.e15. Epub 2019 Mar 18. J Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30944537 Free PMC article.
-
Enrofloxacin Shifts Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolic Profiling and Hinders Recovery from Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Typhimurium Infection in Neonatal Chickens.mSphere. 2020 Sep 9;5(5):e00725-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00725-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32907952 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance in selected bacteria from poultry.Anim Health Res Rev. 2008 Dec;9(2):149-58. doi: 10.1017/S1466252308001552. Anim Health Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 19102788 Review.
Cited by
-
Resistance and Virulence Mechanisms of Escherichia coli Selected by Enrofloxacin in Chicken.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Apr 25;63(5):e01824-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01824-18. Print 2019 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30803968 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Impacts of Antibiotic Exposure on the Diversity of the Gut Microbiota in Chicks.Animals (Basel). 2020 May 21;10(5):896. doi: 10.3390/ani10050896. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32455745 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Characterization of a Nalidixic Acid-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis Strain Causing Persistent Infections in Broiler Chickens.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Sep 1;8:725737. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.725737. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34540936 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Directed Evolution of Anti-Ciprofloxacin ScFv for Immunoassay in Animal-Derived Food.Foods. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):1933. doi: 10.3390/foods10081933. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34441715 Free PMC article.
-
PK/PD integration of florfenicol alone and in combination with doxycycline against Riemerella anatipestifer.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 8;9:975673. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.975673. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36157174 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

