Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management of takotsubo syndrome
- PMID: 28917022
- PMCID: PMC5805795
- DOI: 10.1007/s10286-017-0465-z
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management of takotsubo syndrome
Abstract
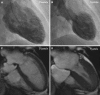
Takotsubo syndrome is a recently recognized acute cardiac disease entity with a clinical presentation resembling that of an acute coronary syndrome. The typical takotsubo syndrome patient has a unique circumferential left (bi-) ventricular contraction abnormality profile that extends beyond a coronary artery supply territory and appears to follow the anatomical cardiac sympathetic innervation. The syndrome predominantly affects postmenopausal women and is often preceded by emotional or physical stress. Patients with predisposing factors such as malignancy and other chronic comorbidities are more prone to suffer from takotsubo syndrome. The pathogenesis of takotsubo syndrome is elusive. Several pathophysiological mechanisms involving myocardial ischemia (multivessel coronary artery spasm, microvascular dysfunction, aborted myocardial infarction), left ventricular outlet tract obstruction, blood-borne catecholamine myocardial toxicity, epinephrine-induced switch in signal trafficking, and autonomic nervous system dysfunction have been proposed. The syndrome is usually reversible; nevertheless, during the acute stage, a substantial number of patients develop severe complications such as arrhythmias, heart failure including pulmonary edema and cardiogenic shock, thromboembolism, cardiac arrest, and rupture. Treatment of precipitating factors, predisposing diseases, and complications is fundamental during the acute stage of the disease. The epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management of takotsubo syndrome are reviewed in this paper.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Broken heart syndrome; Left ventricle ballooning; Neurogenic stunned myocardium; Takotsubo.
Figures




Comment in
-
Metoprolol, propranolol, carvedilol, or labetalol for patients with Takotsubo syndrome?Clin Auton Res. 2018 Feb;28(1):131-132. doi: 10.1007/s10286-017-0482-y. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Clin Auton Res. 2018. PMID: 29110279 No abstract available.
-
Reply to: metoprolol, or propranolol, or carvedilol, or labetalol, for patients with takotsubo syndrome?Clin Auton Res. 2018 Feb;28(1):133-134. doi: 10.1007/s10286-017-0483-x. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Clin Auton Res. 2018. PMID: 29181766 No abstract available.
-
Takotsubo syndrome in the Holy Bible.Clin Auton Res. 2019 Feb;29(1):129. doi: 10.1007/s10286-018-0575-2. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Clin Auton Res. 2019. PMID: 30413907 No abstract available.
References
-
- YH S, De Palma R. Contemporary review on the pathogenesis of takotsubo syndrome: the heart shedding tears: norepinephrine churn and foam at the cardiac sympathetic nerve terminals. Int J Cardiol. 2016;228:528–536. - PubMed
-
- Dote K, Sato H, Tateishi H, Uchida T, Ishihara M. Myocardial stunning due to simultaneous multivessel coronary spasms: a review of 5 cases. J Cardiol. 1991;21:203–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

