miR-206/133b Cluster: A Weapon against Lung Cancer?
- PMID: 28918043
- PMCID: PMC5542379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.06.002
miR-206/133b Cluster: A Weapon against Lung Cancer?
Abstract
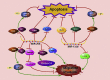
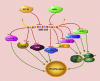
Lung cancer is a deadly disease that ends numerous lives around the world. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of non-coding RNAs involved in a variety of biological processes, such as cell growth, organ development, and tumorigenesis. The miR-206/133b cluster is located on the human chromosome 6p12.2, which is essential for growth and rebuilding of skeletal muscle. The miR-206/133b cluster has been verified to be dysregulated and plays a crucial role in lung cancer. miR-206 and miR-133b participate in lung tumor cell apoptosis, proliferation, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, drug resistance, and cancer treatment. The mechanisms are sophisticated, involving various target genes and molecular pathways, such as MET, EGFR, and the STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signal pathway. Hence, in this review, we summarize the role and potential mechanisms of the miR-206/133b cluster in lung cancer.
Keywords: lung cancer; miR-133b; miR-206; miR-206/133b cluster.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BAP31-Mediated miR-206/133b Cluster Promotes Transendothelial Migration and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 25;24(23):16740. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316740. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069061 Free PMC article.
-
miR-133b Inhibits Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion by Targeting MMP9 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncol Res. 2017 Aug 7;25(7):1109-1116. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14800889609439. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 27938481 Free PMC article.
-
miR-133b, a particular member of myomiRs, coming into playing its unique pathological role in human cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):50193-50208. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16745. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-133b is down-regulated in human osteosarcoma and inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation, migration and invasion, and promotes apoptosis.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 31;8(12):e83571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083571. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24391788 Free PMC article.
-
The lncRNA EGFR-AS1 is linked to migration, invasion and apoptosis in glioma cells by targeting miR-133b/RACK1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109292. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109292. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31545240
Cited by
-
MiR-188-3p and miR-133b Suppress Cell Proliferation in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Post-Transcriptional Suppression of NDRG1.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211033074. doi: 10.1177/15330338211033074. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34355586 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value and Clinicopathological Features of MicroRNA-206 in Various Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 20;2020:2159704. doi: 10.1155/2020/2159704. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33145343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-206 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the c-Met/AKT/GSK-3β pathway.Oncol Lett. 2021 Feb;21(2):147. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12408. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33633805 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-181 Family Members in Stroke: Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 7;26(2):440. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020440. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA‑29a enhances cisplatin sensitivity in non‑small cell lung cancer through the regulation of REV3L.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Feb;19(2):831-840. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9723. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30535450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W., Zheng R., Baade P.D., Zhang S., Zeng H., Bray F., Jemal A., Yu X.Q., He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Travis W.D. IARC Press; 2004. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. - PubMed
-
- Travis W.D. Pathology of lung cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 2011;32:669–692. - PubMed
-
- Rossi G., Mengoli M.C., Cavazza A., Nicoli D., Barbareschi M., Cantaloni C., Papotti M., Tironi A., Graziano P., Paci M. Large cell carcinoma of the lung: clinically oriented classification integrating immunohistochemistry and molecular biology. Virchows Arch. 2014;464:61–68. - PubMed
-
- Beadsmoore C.J., Screaton N.J. Classification, staging and prognosis of lung cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2003;45:8–17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

