In silico interaction analysis of cannabinoid receptor interacting protein 1b (CRIP1b) - CB1 cannabinoid receptor
- PMID: 28918320
- PMCID: PMC5816684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2017.09.006
In silico interaction analysis of cannabinoid receptor interacting protein 1b (CRIP1b) - CB1 cannabinoid receptor
Abstract
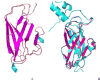
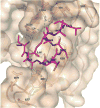
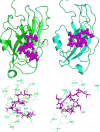
Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein isoform 1b (CRIP1b) is known to interact with the CB1 receptor. Alternative splicing of the CNRIP1 gene produces CRIP1a and CRIP1b with a difference in the third exon only. Exons 1 and 2 encode for a functional domain in both proteins. CRIP1a is involved in regulating CB1 receptor internalization, but the function of CRIP1b is not very well characterized. Since there are significant identities in functional domains of these proteins, CRIP1b is a potential target for drug discovery. We report here predicted structure of CRIP1b followed by its interaction analysis with CB1 receptor by in-silico methods A number of complementary computational techniques, including, homology modeling, ab-initio and protein threading, were applied to generate three-dimensional molecular models for CRIP1b. The computed model of CRIP1b was refined, followed by docking with C terminus of CB1 receptor to generate a model for the CRIP1b- CB1 receptor interaction. The structure of CRIP1b obtained by homology modelling using RHO_GDI-2 as template is a sandwich fold structure having beta sheets connected by loops, similar to predicted CRIP1a structure. The best scoring refined model of CRIP1b in complex with the CB1 receptor C terminus peptide showed favourable polar interactions. The overall binding pocket of CRIP1b was found to be overlapping to that of CRIP1a. The Arg82 and Cys126 of CRIP1b are involved in the majority of hydrogen bond interactions with the CB1 receptor and are possible key residues required for interactions between the CB1 receptor and CRIP1b.
Keywords: CB(1) Receptor; CRIP1a; CRIP1b; Coupled receptor; G Protein; Molecular modeling.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
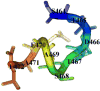

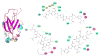
Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein 1a (CRIP1a): Function and Structure.Molecules. 2019 Oct 12;24(20):3672. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203672. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31614728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Interaction between Distal C-Terminal Domain of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor and Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Proteins (CRIP1a/CRIP1b).J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Dec 23;59(12):5294-5303. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00948. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31769975 Free PMC article.
-
CB1 cannabinoid receptor activity is modulated by the cannabinoid receptor interacting protein CRIP 1a.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;72(6):1557-66. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.039263. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17895407
-
Predicting the molecular interactions of CRIP1a-cannabinoid 1 receptor with integrated molecular modeling approaches.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Feb 15;24(4):1158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.12.119. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24461351 Free PMC article.
-
CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor binding studies based on modeling and mutagenesis approaches.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Jul;5(7):651-8. doi: 10.2174/1389557054368754. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16026311 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular docking analysis of the tumor protein beta arrestin-1 with oxadiazole compounds.Bioinformation. 2023 Jan 31;19(1):111-116. doi: 10.6026/97320630019111. eCollection 2023. Bioinformation. 2023. PMID: 37720289 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein 1a (CRIP1a): Function and Structure.Molecules. 2019 Oct 12;24(20):3672. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203672. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31614728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Interaction between Distal C-Terminal Domain of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor and Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Proteins (CRIP1a/CRIP1b).J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Dec 23;59(12):5294-5303. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00948. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31769975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of Cannabinoid Receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:161–202. - PubMed
-
- Ligresti A, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. From phytocannabinoids to cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids: pleiotropic physiological and pathological roles through complex pharmacology. Physiological reviews. 2016;96(4):1593–1659. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

