Alginate oligosaccharide indirectly affects toll-like receptor signaling via the inhibition of microRNA-29b in aneurysm patients after endovascular aortic repair
- PMID: 28919708
- PMCID: PMC5590761
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S140206
Alginate oligosaccharide indirectly affects toll-like receptor signaling via the inhibition of microRNA-29b in aneurysm patients after endovascular aortic repair
Abstract
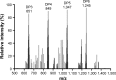
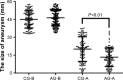
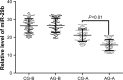
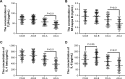
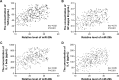
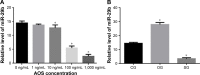
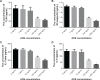
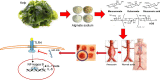
Endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) is often followed by aneurysm recurrence. Alginate oligosaccharide (AOS) has potential antitumor properties as a natural product while the related mechanisms remain unclear. Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is associated with inflammatory activity of aneurysm and may be affected by miR-29b. Thus, inhibitory function of AOS on aneurysms was explored by measuring the important molecules in TLR4 signaling. After EVAR, a total of 248 aortic aneurysm patients were recruited and randomly assigned into two groups: AOS group (AG, oral administration 10-mg AOS daily) and control group (CG, placebo daily). The size of residual aneurysms, aneurysm recurrence, and side effects were investigated. Aneurysm recurrence was determined by Kaplan-Meier analysis. After 2 years, eight and two patients died in the CG and AG, respectively. The sizes of residual aneurysms were significantly larger in the CG than in the AG (P<0.05). The incidence of aneurysm recurrence was also significantly higher in the CG than in the AG (P<0.05). AOS treatment reduced the levels of miR-29b, TLR4, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B), interleukin 1 (IL-1) beta, and interleukin 6 (IL-6). Overexpression and silence of miR-29b increased and reduced the level of TLR4, phospho-p65 NF-kappa B, phospho-p38 MAPK, IL-1 beta, and IL-6. Spearman's rank correlation analysis shows that the level of miR-29b is positively related to the levels of TLR4, NF-kappa B, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 (P<0.05). Thus, AOS represses aneurysm recurrence by indirectly affecting TLR signaling via miR-29b.
Keywords: alginate oligosaccharide; anti-inflammatory agent; aortic aneurysms; microRNA-29b; minimally invasive endovascular repair; mitogen-activated protein kinase; outcome assessment; toll-like receptor signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
miR-29b participates in early aneurysm development in Marfan syndrome.Circ Res. 2012 Jan 20;110(2):312-24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.253740. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22116819
-
Effects of MiR-146a on repair and inflammation in rats with spinal cord injury through the TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;23(11):4558-4563. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18031. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31210336
-
Alginate Oligosaccharide Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Balb/c Mice: Mechanistic Insights.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 May 28;73(21):12679-12689. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c12136. Epub 2025 May 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40367367
-
Open and Endovascular Management of Aortic Aneurysms.Circ Res. 2019 Feb 15;124(4):647-661. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313186. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 30763206 Review.
-
Preparation of alginate oligosaccharides and their biological activities in plants: A review.Carbohydr Res. 2020 Aug;494:108056. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2020.108056. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Carbohydr Res. 2020. PMID: 32559511 Review.
Cited by
-
Alginate oligosaccharides increase boar semen quality by affecting gut microbiota and metabolites in blood and sperm.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 22;13:982152. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.982152. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36071975 Free PMC article.
-
Alginate oligosaccharides improve germ cell development and testicular microenvironment to rescue busulfan disrupted spermatogenesis.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 10;10(7):3308-3324. doi: 10.7150/thno.43189. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32194870 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and Mechanisms of miRNAs in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Signaling Pathways and Clinical Insights.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Jul;26(7):273-287. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01204-8. Epub 2024 May 6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024. PMID: 38709435 Review.
-
Gut-Spleen Axis: Microbiota via Vascular and Immune Pathways Improve Busulfan-Induced Spleen Disruption.mSphere. 2023 Feb 21;8(1):e0058122. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00581-22. Epub 2022 Dec 13. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 36511706 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiently Anti-Obesity Effects of Unsaturated Alginate Oligosaccharides (UAOS) in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice.Mar Drugs. 2019 Sep 17;17(9):540. doi: 10.3390/md17090540. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31533255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butt HZ, Sylvius N, Salem MK, et al. Microarray-based gene expression profiling of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016;52(1):47–55. - PubMed
-
- Gray C, Goodman P, O’Malley MK, O’Donohoe MK, McDonnell CO. Statins promote residual aneurysm sac regression following endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2014;48(2):111–115. - PubMed
-
- Lecler A, Raymond J, Rodriguez-Régent C, et al. Intracranial aneurysms: recurrences more than 10 years after endovascular treatment-A prospective cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Radiology. 2015;277(1):173–180. - PubMed
-
- Elmogy SA, Mazroa JA, Eldawoody HAF. Non-invasive TOF MR angiographic follow up of coiled cerebral aneurysms. Egyptian J Radiol Nuclear Med. 2012;43(1):33–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

