Protective role of quercetin against manganese-induced injury in the liver, kidney, and lung; and hematological parameters in acute and subchronic rat models
- PMID: 28919711
- PMCID: PMC5592961
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S143875
Protective role of quercetin against manganese-induced injury in the liver, kidney, and lung; and hematological parameters in acute and subchronic rat models
Retraction in
-
Protective role of quercetin against manganese-induced injury in the liver, kidney, and lung; and hematological parameters in acute and subchronic rat models [Retraction].Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Mar 18;13:907-908. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S207534. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31118561 Free PMC article.
Abstract
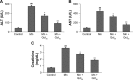
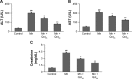
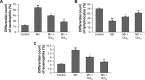
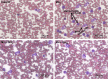
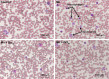
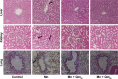
Manganese (Mn) is an important mineral element required in trace amounts for development of the human body, while over- or chronic-exposure can cause serious organ toxicity. The current study was designed to evaluate the protective role of quercetin (Qct) against Mn-induced toxicity in the liver, kidney, lung, and hematological parameters in acute and subchronic rat models. Male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into control, Mn (100 mg/kg for acute model and 15 mg/kg for subchronic model), and Mn + Qct (25 and 50 mg/kg) groups in both acute and subchronic models. Our result revealed that Mn + Qct groups effectively reduced Mn-induced ALT, AST, and creatinine levels. However, Mn + Qct groups had effectively reversed Mn-induced alteration of complete blood count, including red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, platelets, and white blood cells. Meanwhile, the Mn + Qct groups had significantly decreased neutrophil and eosinophil and increased lymphocyte levels relative to the Mn group. Additionally, Mn + Qct groups showed a beneficial effect against Mn-induced macrophages and neutrophils. Our result demonstrated that Mn + Qct groups exhibited protective effects on Mn-induced alteration of GRP78, CHOP, and caspase-3 activities. Furthermore, histopathological observation showed that Mn + Qct groups effectively counteracted Mn-induced morphological change in the liver, kidney, and lung. Moreover, immunohistochemically Mn + Qct groups had significantly attenuated Mn-induced 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine immunoreactivity. Our study suggests that Qct could be a substantially promising organ-protective agent against toxic Mn effects and perhaps against other toxic metal chemicals or drugs.
Keywords: hematological parameters; kidney; liver; lung; manganese; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 15;18(9):1989. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091989. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28914791 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese neurotoxicity and protective effects of resveratrol and quercetin in preclinical research.Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Apr;69(2):322-330. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2016.11.011. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Pharmacol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28183032
-
Protective effects of selenium against cadmium induced hematological disturbances, immunosuppressive, oxidative stress and hepatorenal damage in rats.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2015 Jan;29:104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.05.009. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 24954678
-
Cardioprotective and nephroprotective effects of Quercetin against different toxic agents.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Dec;25(23):7425-7439. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202112_27440. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34919245 Review.
-
Protective effects of Folic acid against reproductive, hematological, hepatic, and renal toxicity induced by Acetamiprid in male Albino rats.Toxicology. 2022 Mar 15;469:153115. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2022.153115. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Toxicology. 2022. PMID: 35124148 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Molecules. 2020 Dec 7;25(23):5772. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235772. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33297540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in serum TIM-3 and complement C3 expression in workers due to Mn exposure.Front Public Health. 2023 Nov 9;11:1289838. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1289838. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38026392 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of quercetin on oxidative stress and liver function in beta-thalassemia major patients receiving desferrioxamine: A double-blind randomized clinical trial.J Res Med Sci. 2019 Oct 25;24:91. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_911_18. eCollection 2019. J Res Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31741663 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of quercetin on seizure, inflammation parameters and oxidative stress in acute on chronic tramadol intoxication.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Oct 19;22(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00532-8. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34666816 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese-methionine chelate improves antioxidant activity, immune system and egg manganese enrichment in the aged laying hens.Vet Med Sci. 2023 Jan;9(1):217-225. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1008. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36409287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keen CL, Ensunsa JL, Watson MH, et al. Nutritional aspects of manganese from experimental studies. Neurotoxicology. 1999;20(2–3):213–223. - PubMed
-
- Aschner M, Aschner JL. Manganese neurotoxicity: cellular effects and blood-brain barrier transport. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1991;15(3):333–340. - PubMed
-
- Hudnell HK. Effects from environmental Mn exposures: a review of the evidence from non-occupational exposure studies. Neurotoxicology. 1999;20(2–3):379–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

