Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of Ki-67 immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28919781
- PMCID: PMC5590776
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S143089
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of Ki-67 immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
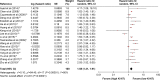
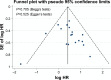
The prognostic significance of Ki-67 in patients with gastric cancer (GC) remains controversial. The aim of our meta-analysis is to evaluate its association with clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic value in patients with GC. PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science were systematically searched up to May 2017. Twenty-two studies including 3,825 patients with GC were analyzed. The meta-analysis indicated that the incidence difference of Ki-67 expression in GC patients was significant when comparing the older group to younger group (odds ratio [OR] =1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.19, 1.75), lymph node positive group to negative group (OR =1.49, 95% CI 1.20, 1.84), the large size tumor group to the small size tumor group (OR =1.27, 95% CI 1.24, 1.68) and the TNM stage III+IV group to TNM stage I+II group (OR =2.28, 95% CI 1.66, 3.12). However, no statistical differences existed in gender. The detection of Ki-67 significantly correlated with the overall survival of patients (hazard ratio =1.51, 95% CI 1.31, 1.72). Our study suggested that Ki-67 overexpression was associated with poor prognosis in GC patients. Ki-67 positive rates may be associated with age, lymph node metastasis, tumor size, and TNM staging system in GC patients.
Keywords: Ki-67; gastric cancer; meta-analysis; prognostic.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





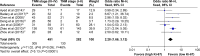
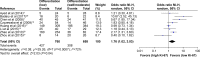
Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological significance of claudin 4 expression in gastric carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 May 27;9:3205-12. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S99461. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27313466 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Int J Cancer. 2015 Jan 1;136(1):21-33. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28954. Epub 2014 May 15. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 24803400
-
The clinicopathological parameters and prognostic significance of HER2 expression in gastric cancer patients: a meta-analysis of literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Mar 21;15(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1132-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28327158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and prognostic significances of cancer stem cell markers in gastric cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 27;21(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01840-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33639931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ki-67/MKI67 as a Predictive Biomarker for Clinical Outcome in Gastric Cancer Patients: an Updated Meta-analysis and Systematic Review involving 53 Studies and 7078 Patients.J Cancer. 2019 Aug 29;10(22):5339-5354. doi: 10.7150/jca.30074. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31632479 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Endoscopy Findings to Identify Early Gastric Cancers with Tumor Budding: A Retrospective Study.J Gastrointest Surg. 2021 Jul;25(7):1706-1715. doi: 10.1007/s11605-020-04862-6. Epub 2020 Nov 9. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021. PMID: 33169320
-
Clinicopathological Features and Postoperative Survival Analysis of Gastric Carcinoma with Neuroendocrine Differentiation.J Oncol. 2022 Aug 17;2022:4440098. doi: 10.1155/2022/4440098. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36035314 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and significance of Her2 and Ki-67 in gastric adenocarcinoma without distant metastasis: a cohort study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 15;20(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01484-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33059614 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Ki-67 expression in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Sep 20;12:1758835920951346. doi: 10.1177/1758835920951346. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014147 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphangiosis Carcinomatosa of the Liver and Extrahepatic Bile Duct Due to Gastric Cancer: A Case Report and Literature Review.Intern Med. 2025 May 1;64(9):1321-1326. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4357-24. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39293974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Martel C, Forman D, Plummer M. Gastric cancer: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013;42(2):219–240. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald JS. Gastric cancer – new therapeutic options. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(1):76–77. - PubMed
-
- Bullwinkel J, Baron-Luhr B, Ludemann A, Wohlenberg C, Gerdes J, Scholzen T. Ki-67 protein is associated with ribosomal RNA transcription in quiescent and proliferating cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(3):624–635. - PubMed
-
- Schonk DM, Kuijpers HJ, van Drunen E, et al. Assignment of the gene(s) involved in the expression of the proliferation-related Ki-67 antigen to human chromosome 10. Hum Genet. 1989;83(3):297–299. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

