Toll-like receptors 7 and 8 expression correlates with the expression of immune biomarkers and positively predicts the clinical outcome of patients with melanoma
- PMID: 28919783
- PMCID: PMC5590684
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S136194
Toll-like receptors 7 and 8 expression correlates with the expression of immune biomarkers and positively predicts the clinical outcome of patients with melanoma
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Toll-like receptors 7 and 8 expression correlates with the expression of immune biomarkers and positively predicts the clinical outcome of patients with melanoma [Corrigendum].Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Nov 16;10:5489. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S151778. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 29180883 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a critical role in cancer, yet the clinical relevance of TLR7/8 expression in melanoma remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of TLR7/8 mRNA levels in melanoma and their correlation with immune biomarkers relevant to disease progression.
Methods: Normalized gene expression and corresponding clinical data of patients with skin cutaneous melanoma were obtained from two public databases: the Cancer Genome Atlas and GSE19234. Log rank (Mantel-Cox) tests were used to perform survival analysis. Multivariate survival analysis was performed on a Cox-regression hazard model. Spearman correlation analyses were used to address the relationship between the expressions of TLR7/8 levels and immune biomarkers in melanoma tumors.
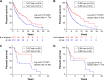
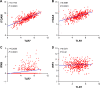
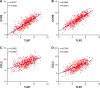
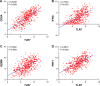
Results: Survival analysis suggested that high levels of TLR7 or TLR8 expression predicted better clinical outcome for melanoma patients (TLR7: HR =1.734, P<0.0001; TLR8: HR =2.072, P<0.0001). Moreover, multivariate survival analysis implicated TLR7 as a prognostic factor independent of age, gender, or pathological stage. Further analysis demonstrated that expression levels of TLR7/8 strongly correlated with that of dendritic cell markers and chemokines/chemokine receptors, including CCR2, CCR5, CCL3, and CCL5. Importantly, expression levels of both TLR7 and TLR8 were also highly correlated with the expressions of CD8 and other functional markers of CD8+ T cells.
Conclusion: High gene expression of TLR7 and TLR8 in melanoma tumors is associated with high expression levels of functional markers of immune cells, which predicts longer overall survival of patients with melanoma. Our results not only provide an important reference for the clinical prognosis of melanoma but also present new implications for the design of melanoma immunotherapy.
Keywords: TLR7; TLR8; immune marker; immunotherapy; melanoma; prognosis; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Hemmi H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett. 2003;85(2):85–95. - PubMed
-
- Song PI, Park YM, Abraham T, et al. Human keratinocytes express functional CD14 and toll-like receptor 4. J Invest Dermat. 2002;119(2):424–432. - PubMed
-
- Bauer S, Pigisch S, Hangel D, Kaufmann A, Hamm S. Recognition of nucleic acid and nucleic acid analogs by Toll-like receptors 7, 8 and 9. Immunobiology. 2008;213(3–4):315–328. - PubMed
-
- Santoni M, Andrikou K, Sotte V, et al. Toll like receptors and pancreatic diseases: from a pathogenetic mechanism to a therapeutic target. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015;41(7):569–576. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

