Exploring bacterial outer membrane barrier to combat bad bugs
- PMID: 28919790
- PMCID: PMC5587131
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S144299
Exploring bacterial outer membrane barrier to combat bad bugs
Abstract
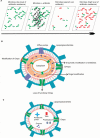
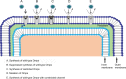
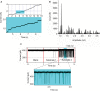
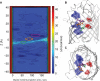
One of the main fundamental mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria comprises an effective change in the membrane permeability to antibiotics. The Gram-negative bacterial complex cell envelope comprises an outer membrane that delimits the periplasm from the exterior environment. The outer membrane contains numerous protein channels, termed as porins or nanopores, which are mainly involved in the influx of hydrophilic compounds, including antibiotics. Bacterial adaptation to reduce influx through these outer membrane proteins (Omps) is one of the crucial mechanisms behind antibiotic resistance. Thus to interpret the molecular basis of the outer membrane permeability is the current challenge. This review attempts to develop a state of knowledge pertinent to Omps and their effective role in antibiotic influx. Further, it aims to study the bacterial response to antibiotic membrane permeability and hopefully provoke a discussion toward understanding and further exploration of prospects to improve our knowledge on physicochemical parameters that direct the translocation of antibiotics through the bacterial membrane protein channels.
Keywords: Gram-negative bacteria; antibiotic resistance; antibiotics; cell envelope; influx; nanopores; protein channels.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrophysiological Insights into Antibiotic Translocation and Resistance: The Impact of Outer Membrane Proteins.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Jul 20;14(7):161. doi: 10.3390/membranes14070161. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding antibiotic resistance via outer membrane permeability.Infect Drug Resist. 2018 Apr 11;11:523-530. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S156995. eCollection 2018. Infect Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29695921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The porin and the permeating antibiotic: a selective diffusion barrier in Gram-negative bacteria.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008 Dec;6(12):893-903. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1994. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18997824 Review.
-
Synergy between Active Efflux and Outer Membrane Diffusion Defines Rules of Antibiotic Permeation into Gram-Negative Bacteria.mBio. 2017 Oct 31;8(5):e01172-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01172-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29089426 Free PMC article.
-
Rationalizing the permeation of polar antibiotics into Gram-negative bacteria.J Phys Condens Matter. 2017 Mar 22;29(11):113001. doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/aa543b. Epub 2017 Feb 3. J Phys Condens Matter. 2017. PMID: 28155846
Cited by
-
β-lactam resistance associated with β-lactamase production and porin alteration in clinical isolates of E. coli and K. pneumoniae.PLoS One. 2021 May 20;16(5):e0251594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251594. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34014957 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Dynamics of Yersinia Adhesin A (YadA) in Outer Membranes Hints at Requirements for β-Barrel Membrane Insertion.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Mar 12;147(10):8618-8628. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c17726. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 40014811 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles in the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance and as Promising Carriers for Therapeutic Agent Delivery.Microorganisms. 2020 May 5;8(5):670. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8050670. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32380740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial Activities of Echinops kebericho Mesfin Tuber Extracts and Isolation of the Most Active Compound, Dehydrocostus Lactone.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 25;11:608672. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.608672. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33597879 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological Insights into Antibiotic Translocation and Resistance: The Impact of Outer Membrane Proteins.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Jul 20;14(7):161. doi: 10.3390/membranes14070161. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kostyanev T, Bonten MJ, O’Brien S, et al. The Innovative Medicines Initiative’s New Drugs for Bad Bugs programme: European public-private partnerships for the development of new strategies to tackle antibiotic resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(2):290–295. - PubMed
-
- Gootz TD. The global problem of antibiotic resistance. Crit Rev Immunol. 2010;30(1):79–93. - PubMed
-
- Stavenger RA, Winterhalter M. TRANSLOCATION project: how to get good drugs into bad bugs. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(228):228ed7. - PubMed
-
- Nikaido H. Role of permeability barriers in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;27(2):197–231. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

