A pilot evaluation of a computer-based psychometric test battery designed to detect impairment in patients with cirrhosis
- PMID: 28919805
- PMCID: PMC5593417
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S140197
A pilot evaluation of a computer-based psychometric test battery designed to detect impairment in patients with cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: Psychometric testing is used to identify patients with cirrhosis who have developed hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Most batteries consist of a series of paper-and-pencil tests, which are cumbersome for most clinicians. A modern, easy-to-use, computer-based battery would be a helpful clinical tool, given that in its minimal form, HE has an impact on both patients' quality of life and the ability to drive and operate machinery (with societal consequences).
Aim: We compared the Cogstate™ computer battery testing with the Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score (PHES) tests, with a view to simplify the diagnosis.
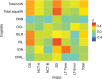
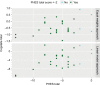
Methods: This was a prospective study of 27 patients with histologically proven cirrhosis. An analysis of psychometric testing was performed using accuracy of task performance and speed of completion as primary variables to create a correlation matrix. A stepwise linear regression analysis was performed with backward elimination, using analysis of variance.
Results: Strong correlations were found between the international shopping list, international shopping list delayed recall of Cogstate and the PHES digit symbol test. The Shopping List Tasks were the only tasks that consistently had P values of <0.05 in the linear regression analysis.
Conclusion: Subtests of the Cogstate battery correlated very strongly with the digit symbol component of PHES in discriminating severity of HE. These findings would indicate that components of the current PHES battery with the international shopping list tasks of Cogstate would be discriminant and have the potential to be used easily in clinical practice.
Keywords: Cogstate™; Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score; cirrhosis; hepatic encephalopathy; minimal hepatic encephalopathy; psychometric testing.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The abstract of this paper was presented at the International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) Conference 2017 as a poster presentation with interim findings. The poster’s abstract was published in Volume 7, Supplement 1 (February 2017) in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology (10.1016/j.jceh.2017.01.037). The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of Turkish norms of psychometric tests for diagnosing minimal hepatic encephalopathy and proposal of a high sensitive screening test battery.Hepatol Int. 2021 Dec;15(6):1442-1455. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10207-5. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Hepatol Int. 2021. PMID: 34085147
-
A simplified psychometric evaluation for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jul;9(7):613-6.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.03.017. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21440091
-
Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score for the Diagnosis of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy in Thai Cirrhotic Patients.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 8;12(2):519. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020519. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675448 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in psychometric tests for screening minimal hepatic encephalopathy: From paper-and-pencil to computer-aided assessment.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019 May;30(5):398-407. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2019.18226. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31060994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualifying and quantifying minimal hepatic encephalopathy.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Dec;31(6):1217-1229. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9726-5. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26412229 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal Dynamic Functional Connectivity in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 20;16:852822. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.852822. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35669490 Free PMC article.
-
Digit Symbol Substitution Test: The Case for Sensitivity Over Specificity in Neuropsychological Testing.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2018 Oct;38(5):513-519. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000941. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30124583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpretable Machine Learning Models for Three-Way Classification of Cognitive Workload Levels for Eye-Tracking Features.Brain Sci. 2021 Feb 9;11(2):210. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11020210. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572232 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal brain functional networks in end-stage renal disease patients with cognitive impairment.Brain Behav. 2021 Apr;11(4):e02076. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2076. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33605530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vilstrup H1, Amodio P, Bajaj J, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60(2):715–735. - PubMed
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy–definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;35(3):716–721. - PubMed
-
- Guerit J, Amantini A, Fischer C, et al. Neurophysiological investigations of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int. 2009;29(6):789–796. - PubMed
-
- Amodio P, Montagnese S, Merkel C. Attention: minimal hepatic encephalopathy and road accidents. Hepatology. 2012;55(4):985–987. - PubMed
-
- Health Protection Agency Health Protection Agency annual report and accounts 2012 to 2013. 2013. [Accessed August 10, 2017]. Available from: www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/246760....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

