Cd226-/- natural killer cells fail to establish stable contacts with cancer cells and show impaired control of tumor metastasis in vivo
- PMID: 28920003
- PMCID: PMC5593708
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1338994
Cd226-/- natural killer cells fail to establish stable contacts with cancer cells and show impaired control of tumor metastasis in vivo
Abstract
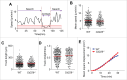
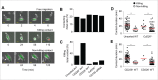
CD226 is an activating receptor expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, CD8+ T cells, and other immune cells. Upon binding to its ligands expressed on target cells, CD226 activates intracellular signaling that triggers cytokine production and degranulation in NK cells. However, the role of CD226 in contact dynamics between NK and cancer cells has remained unclear. Our time-lapse images showed that individual wild-type CD226+ NK cells contacted B16F10 melanoma cells for 23.7 min, but Cd226-/- NK cells only for 12.8 min, although both NK cell subsets showed equal contact frequency over 4 h. On the surface of B16F10 cells, CD226+ cells stayed at the same site with oscillating movement (named stable contact), while Cd226-/- NK cells moved around at a velocity of 4 μm/min (named unstable contact). Consequently, Cd226-/- NK cells did not kill B16F10 cells in vitro and did not inhibit their metastasis into the lung in vivo. Taken together, our data demonstrate that CD226 enables prolonged stable interaction between NK and cancer cells, which is needed for efficient killing of cancer cells.
Keywords: Contact duration; NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity; contact dynamics; contact stability; melanoma.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CD226 regulates natural killer cell antitumor responses via phosphorylation-mediated inactivation of transcription factor FOXO1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 11;115(50):E11731-E11740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1814052115. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30504141 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous expression of the adhesion receptor CD226 on murine NK and T cells and its function in NK-mediated killing of immature dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2009 Jul;86(1):91-101. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1208745. Epub 2009 Apr 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19380711
-
Upregulation of CD226 on subsets of T cells and NK cells is associated with upregulated adhesion molecules and cytotoxic factors in patients with tuberculosis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jul;120:110360. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110360. Epub 2023 May 25. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37244120
-
DNAM-1 and the TIGIT/PVRIG/TACTILE Axis: Novel Immune Checkpoints for Natural Killer Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 23;11(6):877. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060877. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31234588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual-functional capability of cytokine-induced killer cells and application in tumor immunology.Hum Immunol. 2015 May;76(5):385-91. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.09.021. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Hum Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25305457 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional visualization of NK cell-mediated killing of metastatic single tumor cells.Elife. 2022 Feb 3;11:e76269. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76269. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35113018 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of natural cytotoxicity receptors on cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells correlates with effector function.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 16;14:1256404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1256404. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37908353 Free PMC article.
-
The Immune Regulatory Functions of CD226 and Its Implications in Immune-Mediated Diseases.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 14;15(7):1007. doi: 10.3390/biom15071007. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD48-expressing non-small-cell lung cancer cells are susceptible to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity.Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Jan;45(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01365-z. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 34905179
-
TIGIT in cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Sep;8(2):e000957. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000957. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32900861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lakshmikanth T, Burke S, Ali TH, Kimpfler S, Ursini F, Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Umansky V, Paschen A, Sucker A, et al.. NCRs and DNAM-1 mediate NK cell recognition and lysis of human and mouse melanoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 2009; 119:1251-63; PMID:19349689; https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI36022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martinet L, Ferrari De Andrade L, Guillerey C, Lee JS, Liu J, Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Hutchinson DS, Kolesnik TB, Nicholson SE, Huntington ND, et al.. DNAM-1 expression marks an alternative program of NK cell maturation. Cell Rep 2015; 11:85-97; PMID:25818301; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23:225-74; PMID:15771571; https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115526 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horst D, Verweij MC, Davison AJ, Ressing ME, Wiertz EJ. Viral evasion of T cell immunity: Ancient mechanisms offering new applications. Curr Opin Immunol 2011; 23:96-103; PMID:21146386; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2010.11.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Colucci F, Di Santo JP, Leibson PJ. Natural killer cell activation in mice and men: Different triggers for similar weapons? Nat Immunol 2002; 3:807-13; PMID:12205470; https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0902-807 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
