The impact of von Willebrand factor on factor VIII memory immune responses
- PMID: 28920105
- PMCID: PMC5600162
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017009209
The impact of von Willebrand factor on factor VIII memory immune responses
Abstract
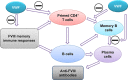
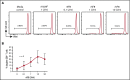
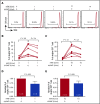
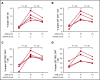
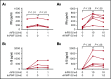
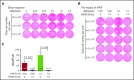
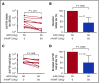
Immune tolerance induction (ITI) with aggressive infusion of factor VIII (FVIII) is the current strategy used to eradicate FVIII inhibitors and restore normal FVIII pharmacokinetics in inhibitor patients. Whether the use of FVIII products containing von Willebrand factor (VWF) will affect the efficacy of ITI is still controversial. In this study, we explored the impact of VWF on FVIII memory immune responses in hemophilia A (HA) mice. A T-cell proliferation assay and cytokine profile analysis were used to study FVIII-primed CD4+ T cells. When CD4+ T cells from primed FVIIInull mice were restimulated with recombinant human FVIII (rhF8) plus recombinant human VWF (rhVWF) in vitro, the percentages of daughter CD4+ T cells were significantly decreased compared with the groups cultured with rhF8 only. Levels of interferon-γ and interleukin 10 were significantly lower in the rhF8 plus rhVWF groups than in the rhF8 groups. When memory B-cell pools from primed FVIIInull mice were cultured with rhF8 with or without rhVWF to induce differentiation of memory B cells into antibody-secreting cells (ASCs), the number of ASCs was significantly lower in the rhF8 plus VWF group than in the rhF8 group. When memory B-cell pools were transferred into NSGF8KO mice followed by rhF8 immunization with or without rhVWF, the titers of anti-F8 inhibitors and total immunoglobulin G were significantly higher in the rhF8 group than in the rhF8 plus rhVWF group, with an average difference of 2.23- and 2.04-fold. Together, our data demonstrate that VWF attenuates FVIII memory immune responses in HA mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of GPIbα on platelet-targeted FVIII gene therapy in hemophilia A mice with pre-existing anti-FVIII immunity.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Mar;17(3):449-459. doi: 10.1111/jth.14379. Epub 2019 Feb 3. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 30609275 Free PMC article.
-
Immune tolerance induced by platelet-targeted factor VIII gene therapy in hemophilia A mice is CD4 T cell mediated.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Oct;15(10):1994-2004. doi: 10.1111/jth.13800. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28799202 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1 along with other platelet contents augments Treg cells to suppress anti-FVIII immune responses in hemophilia A mice.Blood Adv. 2016 Dec 13;1(2):139-151. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016001453. Blood Adv. 2016. PMID: 28164173 Free PMC article.
-
More than a decade of international experience with a pdFVIII/VWF concentrate in immune tolerance.Haemophilia. 2013 Jan;19 Suppl 1:8-11. doi: 10.1111/hae.12050. Haemophilia. 2013. PMID: 23278994 Review.
-
The role of VWF for the success of immune tolerance induction.Thromb Res. 2008;122 Suppl 2:S7-S12. doi: 10.1016/S0049-3848(08)70003-3. Thromb Res. 2008. PMID: 18549910 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-Targeted FVIII Gene Therapy Restores Hemostasis and Induces Immune Tolerance for Hemophilia A.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 12;11:964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00964. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32595633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic Studies of Factor VIII in Chinese Boys with Severe Hemophilia A: A Single-Center Study.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Aug 5;131(15):1780-1785. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.233604. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29848837 Free PMC article.
-
Factor VIII antibody immune complexes modulate the humoral response to factor VIII in an epitope-dependent manner.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1233356. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1233356. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37720212 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose immune tolerance induction alone or with immunosuppressants according to prognostic risk factors in Chinese children with hemophilia A inhibitors.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2021 Jul 14;5(5):e12562. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12562. eCollection 2021 Jul. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34278191 Free PMC article.
-
von Willebrand factor modulates immune complexes and the recall response against factor VIII in a murine hemophilia A model.Blood Adv. 2023 Nov 14;7(21):6771-6781. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010388. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 37756521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiss HJ, Hoyer IW. Von Willebrand factor: dissociation from antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity. Science. 1973;182(4117):1149-1151. - PubMed
-
- Wagner DD. Cell biology of von Willebrand factor. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:217-246. - PubMed
-
- Wise RJ, Dorner AJ, Krane M, Pittman DD, Kaufman RJ. The role of von Willebrand factor multimers and propeptide cleavage in binding and stabilization of factor VIII. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(32):21948-21955. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman RJ, Pipe SW. Regulation of factor VIII expression and activity by von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82(2):201-208. - PubMed
-
- Mannucci PM, Mancuso ME, Santagostino E. How we choose factor VIII to treat hemophilia. Blood. 2012;119(18):4108-4114. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

