Effect of mechanically deboned poultry meat content on technological properties and sensory characteristics of lamb and mutton sausages
- PMID: 28920407
- PMCID: PMC5838331
- DOI: 10.5713/ajas.17.0471
Effect of mechanically deboned poultry meat content on technological properties and sensory characteristics of lamb and mutton sausages
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to develop a value-added product concerning technological and sensory characteristics changes of the use of mechanically deboned poultry meat (MDPM) as meat replacer in lamb and mutton emulsion-type sausages (mortadella).
Methods: Sausages were produced with lamb and mutton and with different contents of MDPM. Six treatments, using lamb or mutton and 0%, 30%, and 60% of MDPM in relation to the meat batter, were produced and analyzed for pH, proximal composition, calcium and residual nitrite content, water activity, 2-thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), instrumental color and texture profile. The sensory profile of the mortadella's was also evaluated by acceptance test and check-all-that-applies (CATA) analysis.
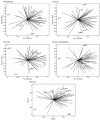
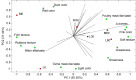
Results: The MDPM addition increased (p<0.05) fat, residual nitrite and calcium content in the all sausage formulations, but mutton sausage had (p<0.05) higher fat and lower moisture content than lamb sausage. The pH, water activity, TBARS index and color was not affected by MDPM additions, while the mutton sausages were significantly redder (higher a*, C*, and lower h°) and darker (lower L*) than lamb sausages. Adding up to 60% of MDPM reduced (p<0.05) sausages hardness and chewiness. Overall, the meat replacement by MDPM increased the sausages acceptance, but the mutton sausage with 30% of MDPM replacer were the most preferred. Consumers related that pink color, glossy appearance, poultry meat-like taste, soft texture, juicy and greasy mouth feel to all sausages contain MDPM according to CATA analysis.
Conclusion: Mutton from culled ewes can be utilized for mortadella production with 30% replacement of lean mutton and fat by MDPM.
Keywords: Check-all-that-applies Analysis; Discarded Animals; Mortadella; Sheep Meat.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- FAO, FAOSTAT Database [internet] Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; [cited 2017 may 5]. Available from: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home.
-
- FAO . Food Outlook Report: June 2017. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 2017.
-
- Olalgaquiaga Perez JR, Bressan MC, Bragagnolo N, et al. Effect of different lamb breed and their slaughter weights on cholesterol, fatty acid profile and proximate composition. Food Sci Technol (Campinas) 2002;22:11–8.
-
- Dutra MP, Palhares PC, Silva JRO, et al. Technological and quality characteristics of cooked ham-type pâté elaborated with sheep meat. Small Rumin Res. 2013;115:56–61.
-
- Guerra ICD, Félex SSS, Meireles BRLM, et al. Evaluation of goat mortadella prepared with different levels of fat and goat meat from discarded animals. Small Rumin Res. 2011;98:59–63.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

