γδ T cells in homeostasis and host defence of epithelial barrier tissues
- PMID: 28920588
- PMCID: PMC5771804
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.101
γδ T cells in homeostasis and host defence of epithelial barrier tissues
Abstract
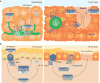
Epithelial surfaces line the body and provide a crucial interface between the body and the external environment. Tissue-resident epithelial γδ T cells represent a major T cell population in the epithelial tissues and are ideally positioned to carry out barrier surveillance and aid in tissue homeostasis and repair. In this Review, we focus on the intraepithelial γδ T cell compartment of the two largest epithelial tissues in the body - namely, the epidermis and the intestine - and provide a comprehensive overview of the crucial contributions of intraepithelial γδ T cells to tissue integrity and repair, host homeostasis and protection in the context of the symbiotic relationship with the microbiome and during pathogen clearance. Finally, we describe epithelium-specific butyrophilin-like molecules and briefly review their emerging role in selectively shaping and regulating epidermal and intestinal γδ T cell repertoires.
Figures



References
-
- Chien YH, Meyer C, Bonneville M. gammadelta T cells: first line of defense and beyond. Annu Rev Immunol. 2014;32:121–155. - PubMed
-
- Jameson JM, Sharp LL, Witherden DA, Havran WL. Regulation of skin cell homeostasis by gamma delta T cells. Front Biosci. 2004;9:2640–2651. - PubMed
-
- van der Flier LG, Clevers H. Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:241–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

