Therapies targeting DNA and RNA in Huntington's disease
- PMID: 28920889
- PMCID: PMC5604739
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30280-6
Therapies targeting DNA and RNA in Huntington's disease
Erratum in
-
Corrections.Lancet Neurol. 2017 Dec;16(12):954. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30367-8. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Lancet Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29165252 No abstract available.
Abstract
No disease-slowing treatment exists for Huntington's disease, but its monogenic inheritance makes it an appealing candidate for the development of therapies targeting processes close to its genetic cause. Huntington's disease is caused by CAG repeat expansions in the HTT gene, which encodes the huntingtin protein; development of therapies to target HTT transcription and the translation of its mRNA is therefore an area of intense investigation. Huntingtin-lowering strategies include antisense oligonucleotides and RNA interference targeting mRNA, and zinc finger transcriptional repressors and CRISPR-Cas9 methods aiming to reduce transcription by targeting DNA. An intrathecally delivered antisense oligonucleotide that aims to lower huntingtin is now well into its first human clinical trial, with other antisense oligonucleotides expected to enter trials in the next 1-2 years and virally delivered RNA interference and zinc finger transcriptional repressors in advanced testing in animal models. Recent advances in the design and delivery of therapies to target HTT RNA and DNA are expected to improve their efficacy, safety, tolerability, and duration of effect in future studies.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
EJW has participated in scientific advisory boards with Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Ionis, Shire, Novartis and Wave Life Sciences and is an investigator on the HTTRx trial. SJT has participated in scientific advisory boards with Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Ionis, Shire, Teva Pharmaceuticals, GSK, Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Heptares Therapeutics, and is the global Principal Investigator on the HTTRx trial, for which she receives no personal salary or fees. All honoraria for these advisory boards were paid through UCL Consultants Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of UCL. Their host clinical institution, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, receives funds as compensation for conducting clinical trials for Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
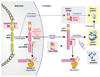
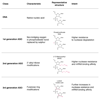
Comment in
-
Sarah Tabrizi: timed to perfection.Lancet Neurol. 2018 Feb;17(2):117. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30303-4. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Lancet Neurol. 2018. PMID: 28916420 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ross CA, Tabrizi SJ. Huntington's disease: from molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. The Lancet Neurology. 2011;10(1):83–98. - PubMed
-
- Wild EJ, Tabrizi SJ. In: Premanifest and Early Huntington’s Disease. Fourth ed Bates G, Jones L, Tabrizi SJ, editors. Huntington's Disease: Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2014.
-
- Ross CA, Aylward EH, Wild EJ, et al. Huntington disease: natural history, biomarkers and prospects for therapeutics. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(4):204–16.
-
- Saudou F, Humbert S. The Biology of Huntingtin. Neuron. 89(5):910–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

