Mice deficient for ERAD machinery component Sel1L develop central diabetes insipidus
- PMID: 28920918
- PMCID: PMC5617649
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI96839
Mice deficient for ERAD machinery component Sel1L develop central diabetes insipidus
Abstract
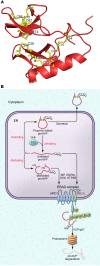
Deficiency of the antidiuretic hormone arginine vasopressin (AVP) underlies diabetes insipidus, which is characterized by the excretion of abnormally large volumes of dilute urine and persistent thirst. In this issue of the JCI, Shi et al. report that Sel1L-Hrd1 ER-associated degradation (ERAD) is responsible for the clearance of misfolded pro-arginine vasopressin (proAVP) in the ER. Additionally, mice with Sel1L deficiency, either globally or specifically within AVP-expressing neurons, developed central diabetes insipidus. The results of this study demonstrate a role for ERAD in neuroendocrine cells and serve as a clinical example of the effect of misfolded ER proteins retrotranslocated through the membrane into the cytosol, where they are polyubiquitinated, extracted from the ER membrane, and degraded by the proteasome. Moreover, proAVP misfolding in hereditary central diabetes insipidus likely shares common physiopathological mechanisms with proinsulin misfolding in hereditary diabetes mellitus of youth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
- ER-associated degradation is required for vasopressin prohormone processing and systemic water homeostasis
Similar articles
-
ER-associated degradation is required for vasopressin prohormone processing and systemic water homeostasis.J Clin Invest. 2017 Oct 2;127(10):3897-3912. doi: 10.1172/JCI94771. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28920920 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of dietary and herbal sourced natural compounds that modulate SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD activity and alleviate protein misfolding in the ER.J Nutr Biochem. 2023 Jan;111:109178. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109178. Epub 2022 Oct 11. J Nutr Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36228974
-
Association of the SEL1L protein transmembrane domain with HRD1 ubiquitin ligase regulates ERAD-L.FEBS J. 2016 Jan;283(1):157-72. doi: 10.1111/febs.13564. Epub 2015 Nov 6. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26471130
-
Role of protein aggregation and degradation in autosomal dominant neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Feb 5;501:110653. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110653. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31785344 Review.
-
The evolving role of ubiquitin modification in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.Biochem J. 2017 Feb 15;474(4):445-469. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160582. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28159894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperglycemia exacerbates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by promoting liver-resident macrophage proinflammatory response via AMPK/PI3K/AKT-mediated oxidative stress.Cell Death Discov. 2019 Jul 19;5:119. doi: 10.1038/s41420-019-0198-y. eCollection 2019. Cell Death Discov. 2019. PMID: 31341645 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from animal models of endocrine disorders caused by defects of protein folding in the secretory pathway.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Jan 1;499:110613. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110613. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31605742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and beyond: The multitasking roles for HRD1 in immune regulation and autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2020 May;109:102423. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102423. Epub 2020 Feb 11. J Autoimmun. 2020. PMID: 32057541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes induces hepatocyte pyroptosis by promoting oxidative stress-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation during liver ischaemia and reperfusion injury.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jun;8(12):739. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-1839. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32647664 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

