Dopamine induces soluble α-synuclein oligomers and nigrostriatal degeneration
- PMID: 28920936
- PMCID: PMC5893155
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4641
Dopamine induces soluble α-synuclein oligomers and nigrostriatal degeneration
Abstract
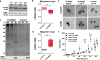
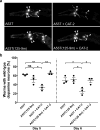
Parkinson's disease (PD) is defined by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the formation of Lewy body inclusions containing aggregated α-synuclein. Efforts to explain dopamine neuron vulnerability are hindered by the lack of dopaminergic cell death in α-synuclein transgenic mice. To address this, we manipulated both dopamine levels and α-synuclein expression. Nigrally targeted expression of mutant tyrosine hydroxylase with enhanced catalytic activity increased dopamine levels without damaging neurons in non-transgenic mice. In contrast, raising dopamine levels in mice expressing human A53T mutant α-synuclein induced progressive nigrostriatal degeneration and reduced locomotion. Dopamine elevation in A53T mice increased levels of potentially toxic α-synuclein oligomers, resulting in conformationally and functionally modified species. Moreover, in genetically tractable Caenorhabditis elegans models, expression of α-synuclein mutated at the site of interaction with dopamine prevented dopamine-induced toxicity. These data suggest that a unique mechanism links two cardinal features of PD: dopaminergic cell death and α-synuclein aggregation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Synuclein and dopamine: the Bonnie and Clyde of Parkinson's disease.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Oct 26;20(11):1514-1515. doi: 10.1038/nn.4660. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29073642 No abstract available.
-
A tango for two: Dopamine and α-synuclein synergy may explain nigrostriatal degeneration in Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2018 Feb;33(2):249. doi: 10.1002/mds.27248. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 29356152 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
AAV1/2-induced overexpression of A53T-α-synuclein in the substantia nigra results in degeneration of the nigrostriatal system with Lewy-like pathology and motor impairment: a new mouse model for Parkinson's disease.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017 Feb 1;5(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0416-x. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28143577 Free PMC article.
-
The Synergistic Effect Study of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and A53T-α-Synuclein: Intranasal LPS Exposure on the A53T-α-Synuclein Transgenic Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):7046-7065. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04020-y. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38367134
-
Intrastriatal injection of pre-formed mouse α-synuclein fibrils into rats triggers α-synuclein pathology and bilateral nigrostriatal degeneration.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Oct;82:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26093169 Free PMC article.
-
The usual suspects, dopamine and alpha-synuclein, conspire to cause neurodegeneration.Mov Disord. 2019 Feb;34(2):167-179. doi: 10.1002/mds.27607. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Mov Disord. 2019. PMID: 30633814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opening avenues for treatment of neurodegenerative disease using post-biotics: Breakthroughs and bottlenecks in clinical translation.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Mar;95:102236. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102236. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38369026 Review.
Cited by
-
From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):986. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020986. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blunting neuroinflammation with resolvin D1 prevents early pathology in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 2;10(1):3945. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11928-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31477726 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in vagal neurons promotes parkinsonian pathology and intercellular α-synuclein transfer.J Clin Invest. 2019 Jun 13;129(9):3738-3753. doi: 10.1172/JCI127330. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31194700 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathology and pathogenesis of extrapyramidal movement disorders: a critical update-I. Hypokinetic-rigid movement disorders.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019 Aug;126(8):933-995. doi: 10.1007/s00702-019-02028-6. Epub 2019 Jun 18. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019. PMID: 31214855 Review.
-
α-Synuclein: A Multifunctional Player in Exocytosis, Endocytosis, and Vesicle Recycling.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jan 28;13:28. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00028. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30745863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ehringer H, Hornykiewicz O. Verteilung von Noradrenalin und Dopamin (3-Hydroxytyramin) im Gehirn des Menschen und ihr Verhalten bei Erkrankungen des extrapyramidalen Systems. Klin Wschr. 1960;38:1236–1239. - PubMed
-
- Graham DG. Oxidative pathways for catecholamines in the genesis of neuromelanin and cytotoxic quinones. Mol Pharmacol. 1978;14:633–43. - PubMed
-
- Jenner P, Olanow CW. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1996;47:S161–70. - PubMed
-
- Dexter DT, Carter CJ, Wells FR, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Lees A, Jenner P, Marsden CD. Basal lipid peroxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 1989;52:381–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

