Growth hormone therapy for people with thalassaemia
- PMID: 28921500
- PMCID: PMC6353149
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012284.pub2
Growth hormone therapy for people with thalassaemia
Update in
-
Growth hormone therapy for people with thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 28;5(5):CD012284. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012284.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32463488 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Thalassaemia is a recessively-inherited blood disorder that leads to anaemia of varying severity. In those affected by the more severe forms, regular blood transfusions are required which may lead to iron overload. Accumulated iron from blood transfusions may be deposited in vital organs including the heart, liver and endocrine organs such as the pituitary glands which can affect growth hormone production. Growth hormone deficiency is one of the factors that can lead to short stature, a common complication in people with thalassaemia. Growth hormone replacement therapy has been used in children with thalassaemia who have short stature and growth hormone deficiency.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and safety of growth hormone therapy in people with thalassaemia.
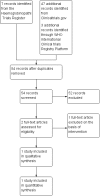
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Haemoglobinopathies Trials Register, compiled from electronic database searches and handsearching of journals and conference abstract books. We also searched the reference lists of relevant articles, reviews and clinical trial registries. Our database and trial registry searches are current to 10 August 2017 and 08 August 2017, respectively.
Selection criteria: Randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials comparing the use of growth hormone therapy to placebo or standard care in people with thalassaemia of any type or severity.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently selected trials for inclusion. Data extraction and assessment of risk of bias were also conducted independently by two authors. The quality of the evidence was assessed using GRADE criteria.
Main results: One parallel trial conducted in Turkey was included. The trial recruited 20 children with homozygous beta thalassaemia who had short stature; 10 children received growth hormone therapy administered subcutaneously on a daily basis at a dose of 0.7 IU/kg per week and 10 children received standard care. The overall risk of bias in this trial was low except for the selection criteria and attrition bias which were unclear. The quality of the evidence for all major outcomes was moderate, the main concern was imprecision of the estimates due to the small sample size leading to wide confidence intervals. Final height (cm) (the review's pre-specified primary outcome) and change in height were not assessed in the included trial. The trial reported no clear difference between groups in height standard deviation (SD) score after one year, mean difference (MD) -0.09 (95% confidence interval (CI) -0.33 to 0.15 (moderate quality evidence). However, modest improvements appeared to be observed in the following key outcomes in children receiving growth hormone therapy compared to control (moderate quality evidence): change between baseline and final visit in height SD score, MD 0.26 (95% CI 0.13 to 0.39); height velocity, MD 2.28 cm/year (95% CI 1.76 to 2.80); height velocity SD score, MD 3.31 (95% CI 2.43 to 4.19); and change in height velocity SD score between baseline and final visit, MD 3.41 (95% CI 2.45 to 4.37). No adverse effects of treatment were reported in either group; however, while there was no clear difference between groups in the oral glucose tolerance test at one year, fasting blood glucose was significantly higher in the growth hormone therapy group compared to control, although both results were still within the normal range, MD 6.67 mg/dL (95% CI 2.66 to 10.68). There were no data beyond the one-year trial period.
Authors' conclusions: A small single trial contributed evidence of moderate quality that the use of growth hormone for a year may improve height velocity of children with thalassaemia although height SD score in the treatment group was similar to the control group. There are no randomised controlled trials in adults or trials that address the use of growth hormone therapy over a longer period and assess its effect on final height and quality of life. The optimal dosage of growth hormone and the ideal time to start this therapy remain uncertain. Large well-designed randomised controlled trials over a longer period with sufficient duration of follow up are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
JH received a honorarium for giving a talk in an event sponsored by a pharmaceutical company related to growth hormone.
CFN, NML, SLT, AR, PM and MKT have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
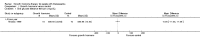
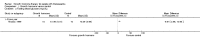
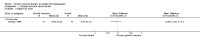





Similar articles
-
Growth hormone therapy for people with thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 28;5(5):CD012284. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012284.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32463488 Free PMC article.
-
Folate supplementation in people with sickle cell disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 16;3(3):CD011130. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011130.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29546732 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium channel blockers for preventing cardiomyopathy due to iron overload in people with transfusion-dependent beta thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 17;11(11):CD011626. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011626.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37975597 Free PMC article.
-
Deferasirox for managing iron overload in people with thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 15;8(8):CD007476. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007476.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28809446 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for improving adherence to iron chelation therapy in people with sickle cell disease or thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 8;5(5):CD012349. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012349.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 6;3:CD012349. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012349.pub3. PMID: 29737522 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
An ICET-A survey on occult and emerging endocrine complications in patients with β-thalassemia major: Conclusions and recommendations.Acta Biomed. 2019 Jan 15;89(4):481-489. doi: 10.23750/abm.v89i4.7774. Acta Biomed. 2019. PMID: 30657116 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
-
- Arcasoy A, Ocal G, Kemahli S, Berberoglu M, Yildirmak Y, Canatan D, et al. Recombinant human growth hormone treatment in children with thalassemia major. Pediatrics International 1999;41(6):655‐61. [CFGD Register: TH33] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
-
- Beshlawy A, Mohtar G, Abd El Ghafar E, Abd El Dayem SM, Sayed MH, Aly AA, et al. Assessment of puberty in relation to L‐carnitine and hormonal replacement therapy in beta‐thalassemic patients. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2008;54(6):375‐81. [CFGD Register: TH114] - PubMed
Additional references
-
- V Abbassi. Growth and normal puberty. Pediatrics 1998;1(102(Supplement 3)):507‐11. - PubMed
-
- Anita S. Growth retardation in thalassemia major patients. International Journal of Human Genetics 2003;3:237‐46.
-
- Belhoul KM, Bakir ML, Saned MS, Kadhim AM, Musallam KM, Taher AT. Serum ferritin levels and endocrinopathy in medically treated patients with beta thalassemia major. Annals of Hematology 2012;91(7):1107‐14. - PubMed
-
- Bell J, Parker KL, Swinford RD, Hoffman AR, Maneatis T, Lippe B. Long term safety of recombinant human growth hormone in children. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2010;95(1):167‐77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

