Disruption of perineuronal nets increases the frequency of sharp wave ripple events
- PMID: 28921856
- PMCID: PMC6047756
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.22804
Disruption of perineuronal nets increases the frequency of sharp wave ripple events
Abstract
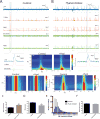
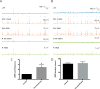
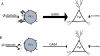
Hippocampal sharp wave ripples (SWRs) represent irregularly occurring synchronous neuronal population events that are observed during phases of rest and slow wave sleep. SWR activity that follows learning involves sequential replay of training-associated neuronal assemblies and is critical for systems level memory consolidation. SWRs are initiated by CA2 or CA3 pyramidal cells (PCs) and require initial excitation of CA1 PCs as well as participation of parvalbumin (PV) expressing fast spiking (FS) inhibitory interneurons. These interneurons are relatively unique in that they represent the major neuronal cell type known to be surrounded by perineuronal nets (PNNs), lattice like structures composed of a hyaluronin backbone that surround the cell soma and proximal dendrites. Though the function of the PNN is not completely understood, previous studies suggest it may serve to localize glutamatergic input to synaptic contacts and thus influence the activity of ensheathed cells. Noting that FS PV interneurons impact the activity of PCs thought to initiate SWRs, and that their activity is critical to ripple expression, we examine the effects of PNN integrity on SWR activity in the hippocampus. Extracellular recordings from the stratum radiatum of horizontal murine hippocampal hemisections demonstrate SWRs that occur spontaneously in CA1. As compared with vehicle, pre-treatment (120 min) of paired hemislices with hyaluronidase, which cleaves the hyaluronin backbone of the PNN, decreases PNN integrity and increases SWR frequency. Pre-treatment with chondroitinase, which cleaves PNN side chains, also increases SWR frequency. Together, these data contribute to an emerging appreciation of extracellular matrix as a regulator of neuronal plasticity and suggest that one function of mature perineuronal nets could be to modulate the frequency of SWR events.
Keywords: PV interneuron; chondrotinase; hippocampus; hyaluronidase; protease.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
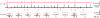

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory Parvalbumin Basket Cell Activity is Selectively Reduced during Hippocampal Sharp Wave Ripples in a Mouse Model of Familial Alzheimer's Disease.J Neurosci. 2020 Jun 24;40(26):5116-5136. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0425-20.2020. Epub 2020 May 21. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32439703 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of sharp wave initiation and ripple generation.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 20;34(34):11385-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0867-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25143618 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Sharp Wave-Ripple Events by Disinhibition.J Neurosci. 2020 Oct 7;40(41):7811-7836. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2174-19.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32913107 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic Remodeling of Perineuronal Nets: Effects on Synaptic Plasticity and Neuronal Population Dynamics.Neural Plast. 2018 Feb 4;2018:5735789. doi: 10.1155/2018/5735789. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29531525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perineuronal Nets and Metal Cation Concentrations in the Microenvironments of Fast-Spiking, Parvalbumin-Expressing GABAergic Interneurons: Relevance to Neurodevelopment and Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 18;11(8):1235. doi: 10.3390/biom11081235. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture promotes the repair of the damaged spinal cord in mice by mediating neurocan-perineuronal net.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jan;30(1):e14468. doi: 10.1111/cns.14468. Epub 2023 Nov 10. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37950551 Free PMC article.
-
A glial perspective on the extracellular matrix and perineuronal net remodeling in the central nervous system.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Oct 20;16:1022754. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1022754. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36339816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix remodeling with stress and depression: Studies in human, rodent and zebrafish models.Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Jun;53(12):3879-3888. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14910. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32673433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Perineuronal Nets in Physiology and Disease: Insights from Recent Studies.Cells. 2025 Feb 20;14(5):321. doi: 10.3390/cells14050321. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measuring Sharp Waves and Oscillatory Population Activity With the Genetically Encoded Calcium Indicator GCaMP6f.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jun 19;13:274. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00274. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31275115 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

