Efficacy and safety of the addition of ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin and sitagliptin: The VERTIS SITA2 placebo-controlled randomized study
- PMID: 28921862
- PMCID: PMC5836931
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13116
Efficacy and safety of the addition of ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin and sitagliptin: The VERTIS SITA2 placebo-controlled randomized study
Abstract
Aims: To assess ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes who are inadequately controlled by metformin and sitagliptin.
Materials and methods: In this double-blind randomized study (Clinicaltrials.gov NCT02036515), patients (glycated haemoglobin [HbA1c] 7.0% to 10.5% [53-91 mmol/mol] receiving metformin ≥1500 mg/d and sitagliptin 100 mg/d; estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2 ) were randomized to ertugliflozin 5 mg once-daily, 15 mg once-daily or placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint was change from baseline in HbA1c at Week 26; treatment was continued until Week 52.
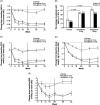
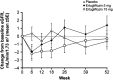
Results: A total of 464 patients were randomized (mean baseline HbA1c, 8.0% [64.3 mmol/mol]; eGFR, 87.9 mL/min/1.73 m2 ). After 26 weeks, placebo-adjusted least squares (LS) mean changes in HbA1c from baseline were -0.7% (-7.5 mmol/mol) and -0.8% (-8.3 mmol/mol) for ertugliflozin 5 and 15 mg, respectively (both P < .001); 17.0%, 32.1% and 39.9% of patients receiving placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg or ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively, had HbA1c <7.0% (53 mmol/mol). Significant reductions in fasting plasma glucose, body weight (BW) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) were observed with ertugliflozin relative to placebo. The positive effects of ertugliflozin on glycaemic control, BW and SBP were maintained through Week 52. A higher incidence of genital mycotic infections was observed in male and female patients receiving ertugliflozin (3.7%-14.1%) vs placebo (0%-1.9%) through Week 52. The incidence of urinary tract infections, symptomatic hypoglycaemia and hypovolaemia adverse events were not meaningfully different across groups.
Conclusions: Ertugliflozin added to metformin and sitagliptin was well-tolerated, and provided clinically meaningful, durable glycaemic control, BW and SBP reductions vs placebo over 52 weeks.
Keywords: DPP-IV inhibitor; SGLT2 inhibitor; drug development; glycaemic control; sitagliptin; type 2 diabetes.
© 2017 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
S. D.‐J. is the principal investigator/coinvestigator for clinical trials contracts with the University of Tennessee, funded by AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; is a consultant/advisory board member for Amgen, Merck & Co., Inc., Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
R. E. was an employee of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey, at the time the study was conducted. B. L., J. L., G. A., J. J., D. H., S. H., G. G. and S. S. E. are employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey and may own stock and/or hold stock options in the company. Y. L. is an employee of MSD R&D (China) Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey, and may own stock and/or hold stock options in the Company. S. G. T. and J. P. M. are employees and shareholders in Pfizer Inc.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . Standards of medical care in diabetes – 2016. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(suppl 1):S1–S112. - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. The incretin system: glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2006;368:1696–1705. - PubMed
-
- Karasik A, Aschner P, Katzeff H, Davies MJ, Stein PP. Sitagliptin, a DPP‐4 inhibitor for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: a review of recent clinical trials. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24:489–496. - PubMed
-
- Deacon CF. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition with sitagliptin: a new therapy for type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16:533–545. - PubMed
-
- Scott R, Loeys T, Davies MJ, Engel SS. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:959–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

