Chronic kidney disease and incident apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among blacks: Data from the Jackson Heart Study
- PMID: 28921875
- PMCID: PMC5693725
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13065
Chronic kidney disease and incident apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among blacks: Data from the Jackson Heart Study
Abstract
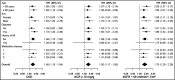
It is unclear whether black patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) vs those without CKD who take antihypertensive medication have an increased risk for apparent treatment-resistant hypertension (aTRH). The authors analyzed 1741 Jackson Heart Study participants without aTRH taking antihypertensive medication at baseline. aTRH was defined as uncontrolled blood pressure while taking three antihypertensive medication classes or taking four or more antihypertensive medication classes, regardless of blood pressure level. CKD was defined as an albumin to creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g or estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 . Over 8 years, 20.1% of participants without CKD and 30.5% with CKD developed aTRH. The multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for aTRH comparing participants with CKD vs those without CKD was 1.45 (95% CI, 1.12-1.86). Participants with an albumin to creatinine ratio ≥30 vs <30 mg/g (hazard ratio, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.04-2.00) and estimated glomerular filtration rate of 45 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m2 and <45 vs ≥60mL/min/1.73 m2 (hazard ratio, 1.60 [95% CI, 1.16-2.20] and 2.05 [95% CI, 1.28-3.26], respectively) were more likely to develop aTRH.
Keywords: blood pressure; chronic kidney disease; treatment-resistant hypertension.
©2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Phenotypes in Adults Taking Antihypertensive Medication with and without CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Apr 7;15(4):501-510. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08840719. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32217635 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of apparent treatment-resistant hypertension among individuals with CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Sep;8(9):1583-90. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00550113. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23868902 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, phenotypic characteristics and prognostic role of apparent treatment resistant hypertension in the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) study.J Hum Hypertens. 2023 May;37(5):345-353. doi: 10.1038/s41371-022-00701-0. Epub 2022 May 9. J Hum Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 35534618
-
Incident ESRD and treatment-resistant hypertension: the reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke (REGARDS) study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 May;63(5):781-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.11.016. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24388119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apparent treatment-resistant hypertension and chronic kidney disease: another cardiovascular-renal syndrome?Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014 Nov;21(6):489-99. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 25443574 Review.
Cited by
-
Etiology and Management of Treatment-Resistant Hypertension in African American Adults ≥18 Years: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2022 Sep 25;14(9):e29566. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29566. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36312638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Apparent Treatment-Resistant Hypertension With Differential Risk of End-Stage Kidney Disease Across Racial Groups in the Million Veteran Program.Hypertension. 2021 Aug;78(2):376-386. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16181. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Hypertension. 2021. PMID: 34148359 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association.Circulation. 2023 Feb 21;147(8):e93-e621. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 36695182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population-Attributable Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Associated With Hypertension in Black Adults.JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Dec 1;4(12):1194-1202. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.3773. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31642869 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of mangiferin against kidney disorders and its mechanism of action: A review.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar;29(3):1530-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.016. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35280538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008;51:1403‐1419. - PubMed
-
- Parikh NI, Hwang SJ, Larson MG, Meigs JB, Levy D, Fox CS. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in chronic kidney disease: overall burden and rates of treatment and control. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1884‐1891. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Wei GL, McQuillan G, et al. Prevalence of high blood pressure and elevated serum creatinine level in the United States: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988‐1994). Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1207‐1216. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

