A Critical Assessment of Exosomes in the Pathogenesis and Stratification of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 28922170
- PMCID: PMC5676982
- DOI: 10.3233/JPD-171176
A Critical Assessment of Exosomes in the Pathogenesis and Stratification of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
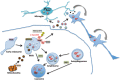
Extracellular vesicles including exosomes are released by a variety of cell types including neurons and exhibit molecular profiles that reflect normal and disease states. As their content represents a snapshot of the intracellular milieu, they could be exploited as biomarkers of the otherwise inaccessible brain microenvironment. In addition they may contribute to the progression of neurodegenerative disorders by facilitating the spread of misfolded proteins at distant sites or activating immune cells. This review summarizes recent advances in the study of exosomes in Parkinson's disease pathophysiology and their potential as disease biomarkers.
Keywords: Aggregation; LRRK2; alpha-synuclein; biomarker; exosome; neurodegeneration.
Figures
References
-
- Hely MA, Reid WG, Adena MA, Halliday GM, & Morris JG (2008) The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: The inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov Disord 23, 837–844. - PubMed
-
- Tofaris GK (2012) Lysosome-dependent pathways as a unifying theme in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27, 1364–1369. - PubMed
-
- Perrett RM, Alexopoulou Z, & Tofaris GK (2015) The endosomal pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 66, 21–28. - PubMed
-
- Colombo M, Raposo G, & Théry C (2014) Biogenesis, secretion and intracellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30, 255–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

