Targets for immunotherapy of liver cancer
- PMID: 28923358
- PMCID: PMC5857416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.09.007
Targets for immunotherapy of liver cancer
Abstract
Drug development in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been characterised by many failures in the past. Despite good rationales and promising phase II data, many phase III trials failed. Immunotherapy represents an alternative treatment approach that has been successful in many different cancer types. As an inflammation induced cancer, HCC represents a very interesting target for immune based approaches. Indeed, early results from clinical trials testing immune checkpoint inhibitors are not only promising, but have already led to evaluation in a phase III setting. Herein, we summarise our current knowledge on the rationale, mechanism of action and clinical data for immune checkpoint blockade in HCC. In addition, we provide an overview of other novel immune based approaches currently under development for the treatment of HCC, such as adoptive cell based and antibody-based approaches.
Keywords: Cancer; HCC; Immunotherapy.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Bruno Sangro has received consulting and/or lecture fees from Adaptimmune, Astra Zeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Medimmune and Onxeo.
Figures
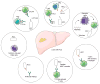
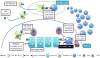
References
-
- Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang Y-H, Bodoky G, et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32453-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Greten TF, Manns MP, Korangy F. Immunotherapy of HCC. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2008;3:31–9. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

