GJA1-20k Arranges Actin to Guide Cx43 Delivery to Cardiac Intercalated Discs
- PMID: 28923791
- PMCID: PMC5790189
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311955
GJA1-20k Arranges Actin to Guide Cx43 Delivery to Cardiac Intercalated Discs
Abstract
Rationale: Delivery of Cx43 (connexin 43) to the intercalated disc is a continuous and rapid process critical for intercellular coupling. By a pathway of targeted delivery involving microtubule highways, vesicles of Cx43 hemichannels are efficiently trafficked to adherens junctions at intercalated discs. It has also been identified that actin provides rest stops for Cx43 forward trafficking and that Cx43 has a 20 kDa internally translated small C terminus isoform, GJA1-20k (Gap Junction Protein Alpha 1- 20 kDa), which is required for full-length Cx43 trafficking, but by an unknown mechanism.
Objective: We explored the mechanism by which the GJA1-20k isoform is required for full-length Cx43 forward trafficking to intercalated discs.
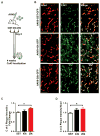
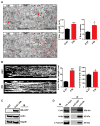
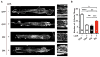
Methods and results: Using an in vivo Adeno-associated virus serotype 9-mediated gene transfer system, we confirmed in whole animal that GJA1-20k markedly increases endogenous myocardial Cx43 gap junction plaque size at the intercalated discs. In micropatterned cell pairing systems, we found that exogenous GJA1-20k expression stabilizes filamentous actin without affecting actin protein expression and that GJA1-20k complexes with both actin and tubulin. We also found that filamentous actin regulates microtubule organization as inhibition of actin polymerization with a low dose of latrunculin A disrupts the targeting of microtubules to cell-cell junctions. GJA1-20k protects actin filament from latrunculin A disruption, preserving microtubule trajectory to the cell-cell border. For therapeutic implications, we found that prior in vivo Adeno-associated virus serotype 9-mediated gene delivery of GJA1-20k to the heart protects Cx43 localization to the intercalated discs against acute ischemic injury.
Conclusions: The internally translated GJA1-20k isoform stabilizes actin filaments, which guides growth trajectories of the Cx43 microtubule trafficking machinery, increasing delivery of Cx43 hemichannels to cardiac intercalated discs. Exogenous GJA1-20k helps to maintain cell-cell coupling in instances of anticipated myocardial ischemia.
Keywords: adherens junctions; connexin 43; cytoskeleton; gap junctions; latrunculin A; trafficking; tubulin.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Porter KR, Novikoff AB. The 1974 nobel prize for physiology or medicine. Science. 1974;186:516–20. - PubMed
-
- Heemels MT. Medicine Nobel goes to pioneer of protein guidance mechanisms. Nature. 1999;401:625. - PubMed
-
- Ferro-Novick S, Brose N. Nobel 2013 Physiology or medicine: Traffic control system within cells. Nature. 2013;504:98. - PubMed
-
- Unwin PN, Zampighi G. Structure of the junction between communicating cells. Nature. 1980;283:545–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

