Is Chronic Dialysis the Right Hard Renal End Point To Evaluate Renoprotective Drug Effects?
- PMID: 28923834
- PMCID: PMC5628725
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09590916
Is Chronic Dialysis the Right Hard Renal End Point To Evaluate Renoprotective Drug Effects?
Abstract
Background and objectives: RRT and doubling of serum creatinine are considered the objective hard end points in nephrology intervention trials. Because both are assumed to reflect changes in the filtration capacity of the kidney, drug effects, if present, are attributed to kidney protection. However, decisions to start RRT are not only on the basis of filtration capacity of the kidney, but also on other factors. We therefore compared the time to RRT with the time to a fixed eGFR threshold and assessed the effect of the renoprotective drug irbesartan on both components.
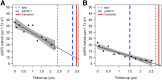
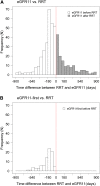
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Post hoc analysis of two clinical trials, the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial (IDNT) and Reduction of End points in Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan Trial, in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. The time to a predefined eGFR level of 11 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (eGFR11), calculated by within-patient linear regression, was compared with the time to RRT or sustained serum creatinine ≥6 mg/dl.
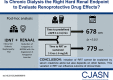
Results: A large difference was observed in the median time to RRT (779 days) compared with eGFR11 (678 days; P=0.01). We also observed a large variation in the difference between the time to RRT and eGFR11. In IDNT, the hazard ratio for the effect of irbesartan on the serum creatinine ≥6.0 mg/dl end point was 0.60 (95% confidence interval, 0.39 to 0.91; P=0.02), whereas it was smaller for the RRT end point (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.58 to 1.07; P=0.12).
Conclusions: This study shows a difference in the time to RRT and a fixed eGFR threshold, and shows that the effect of an angiotensin receptor blocker on a filtration-based end point versus RRT varies. This implies that evaluating renoprotective effects of drugs with a combined RRT and doubling of serum creatinine end point may result in evaluating other effects beyond renoprotection alone. Future trials should consider registering all parameters that lead to RRT decisions.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Biphenyl Compounds; Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2; Diabetic Nephropathies; Humans; Linear Models; Losartan; Renal Replacement Therapy; Tetrazoles; creatinine; glomerular filtration rate; irbesartan; kidney; nephrology; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Rethinking End Points in Clinical Trials of Renoprotective Medication.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Oct 6;12(10):1561-1562. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09040817. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28923832 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD; The Collaborative Study Group : The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 329: 1456–1462, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Lambers Heerspink HJ, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D: Is doubling of serum creatinine a valid clinical ‘hard’ endpoint in clinical nephrology trials? Nephron Clin Pract 119: c195–c199, discussion c199, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Grunfeld JP, Keane WF, Kurokawa K, McGill JB, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Ribeiro AB, Schluchter MD, Snavely D, Zhang Z, Simpson R, Ramjit D, Shahinfar S; RENAAL Study Investigators : The losartan renal protection study--Rationale, study design and baseline characteristics of RENAAL (Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan). J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 1: 328–335, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Rodby RA, Rohde RD, Clarke WR, Hunsicker LG, Anzalone DA, Atkins RC, Ritz E, Lewis EJ; For the Collaborative Study Group : The Irbesartan type II diabetic nephropathy trial: Study design and baseline patient characteristics. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15: 487–497, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S; RENAAL Study Investigators : Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 345: 861–869, 2001 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

