IgH isotype-specific B cell receptor expression influences B cell fate
- PMID: 28923960
- PMCID: PMC5635877
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1704962114
IgH isotype-specific B cell receptor expression influences B cell fate
Erratum in
-
Correction for Tong et al., IgH isotype-specific B cell receptor expression influences B cell fate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 7;114(45):E9750-E9751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717714114. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29078428 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Ig heavy chain (IgH) isotypes (e.g., IgM, IgG, and IgE) are generated as secreted/soluble antibodies (sIg) or as membrane-bound (mIg) B cell receptors (BCRs) through alternative RNA splicing. IgH isotype dictates soluble antibody function, but how mIg isotype influences B cell behavior is not well defined. We examined IgH isotype-specific BCR function by analyzing naturally switched B cells from wild-type mice, as well as by engineering polyclonal Ighγ1/γ1 and Ighε/ε mice, which initially produce IgG1 or IgE from their respective native genomic configurations. We found that B cells from wild-type mice, as well as Ighγ1/γ1 and Ighε/ε mice, produce transcripts that generate IgM, IgG1, and IgE in an alternative splice form bias hierarchy, regardless of cell stage. In this regard, we found that mIgμ > mIgγ1 > mIgε, and that these BCR expression differences influence respective developmental fitness. Restrained B cell development from Ighγ1/γ1 and Ighε/ε mice was proportional to sIg/mIg ratios and was rescued by enforced expression of the respective mIgs. In addition, artificially enhancing BCR signal strength permitted IgE+ memory B cells-which essentially do not exist under normal conditions-to provide long-lived memory function, suggesting that quantitative BCR signal weakness contributes to restraint of IgE B cell responses. Our results indicate that IgH isotype-specific mIg/BCR dosage may play a larger role in B cell fate than previously anticipated.
Keywords: B cell; BCR; IgE; antibody; memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
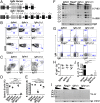
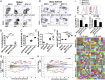
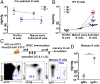
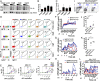
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous expression of germline gamma1 and epsilon immunoglobulin heavy chain transcripts in single murine splenic B-cells.Mol Immunol. 1997 Aug-Sep;34(12-13):919-27. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(97)00106-5. Mol Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9464527
-
Human B-cell isotype switching origins of IgE.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Feb;137(2):579-586.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Aug 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26309181 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 promotes B lymphocyte Ig isotype switching to IgE.J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):162-70. J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7995935
-
Repertoire selection by pre-B-cell receptors and B-cell receptors, and genetic control of B-cell development from immature to mature B cells.Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:33-46. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933589 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of IgE Class Switch Recombination.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;388:21-37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-13725-4_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25553793 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Cell-Based High-Throughput Ig and TCR Repertoire Sequencing Analysis in Rhesus Macaques.J Immunol. 2022 Feb 1;208(3):762-771. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100824. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34987112 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell receptor physical properties affect relative IgG1 and IgE responses in mouse egg allergy.Mucosal Immunol. 2022 Jun;15(6):1375-1388. doi: 10.1038/s41385-022-00567-y. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Mucosal Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36114245 Free PMC article.
-
B Cell Intrinsic Mechanisms Constraining IgE Memory.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 13;8:1277. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01277. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29180995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-classical B Cell Memory of Allergic IgE Responses.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 26;10:715. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00715. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31105687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgE and IgG Antibodies as Regulators of Mast Cell and Basophil Functions in Food Allergy.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 11;11:603050. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.603050. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33362785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reth M. Antigen receptors on B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:97–121. - PubMed
-
- Peterson ML. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene regulation through polyadenylation and splicing competition. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2:92–105. - PubMed
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
-
- Tong P, Wesemann DR. Molecular mechanisms of IgE class switch recombination. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;388:21–37. - PubMed
-
- Nutt SL, Hodgkin PD, Tarlinton DM, Corcoran LM. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:160–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

