Insights into the functionality of endophytic actinobacteria with a focus on their biosynthetic potential and secondary metabolites production
- PMID: 28924162
- PMCID: PMC5603540
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12235-4
Insights into the functionality of endophytic actinobacteria with a focus on their biosynthetic potential and secondary metabolites production
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Insights into the functionality of endophytic actinobacteria with a focus on their biosynthetic potential and secondary metabolites production.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 12;8(1):4650. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22947-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29531340 Free PMC article.
Abstract
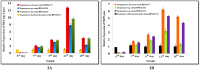
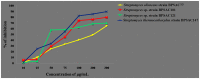
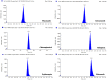
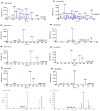
Endophytic actinobacteria play an important role in growth promotion and development of host plant by producing enormous quantities of novel bioactive natural products. In the present investigation, 169 endophytic actinobacteria were isolated from endospheric tissues of Rhynchotoechum ellipticum. Based on their antimicrobial potential, 81 strains were identified by 16rRNA gene analysis, which were taxonomically grouped into 15 genera. All identified strains were screened for their plant growth promoting attributes and, for the presence of modular polyketide synthases (PKSI, PKSII and nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) gene clusters to correlate the biosynthetic genes with their functional properties. Expression studies and antioxidant potential for four representative strains were evaluated using qRT-PCR and DPPH assay respectively. Additionally, six antibiotics (erythromycin, ketoconazole, fluconazole, chloramphenicol, rifampicin and miconazole) and nine phenolic compounds (catechin, kaempferol, chebulagic acid, chlorogenic acid, Asiatic acid, ferulic acid, arjunic acid, gallic acid and boswellic acid) were detected and quantified using UHPLC-QqQLIT-MS/MS. Furthermore, three strains (BPSAC77, 121 and 101) showed the presence of the anticancerous compound paclitaxel which was reported for the first time from endophytic actinobacteria. This study provides a holistic picture, that endophytic actinobacteria are rich bacterial resource for bioactive natural products, which has a great prospective in agriculture and pharmaceutical industries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Rai, M., Agarkar, G. & Rathod, D. Multiple applications of endophytic Colletotrichum species occurring in medicinal plants, in novel plant bioresources: Applications in food, medicine and cosmetics. In: Gurib-Fakim. A. (ed.) Novel plant bioresources. Wiley, Chichester, pp 227–236 (2014a).
-
- Rai M, et al. Fungal growth promotor endophytes: apragmatic approach towards sustainable food and agriculture. Symbiosis. 2014;62:63–79. doi: 10.1007/s13199-014-0273-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

