Common and dissociable regional cerebral blood flow differences associate with dimensions of psychopathology across categorical diagnoses
- PMID: 28924181
- PMCID: PMC5858960
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2017.174
Common and dissociable regional cerebral blood flow differences associate with dimensions of psychopathology across categorical diagnoses
Abstract
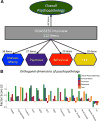
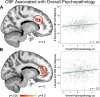
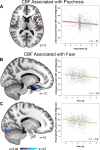
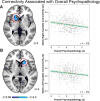
The high comorbidity among neuropsychiatric disorders suggests a possible common neurobiological phenotype. Resting-state regional cerebral blood flow (CBF) can be measured noninvasively with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and abnormalities in regional CBF are present in many neuropsychiatric disorders. Regional CBF may also provide a useful biological marker across different types of psychopathology. To investigate CBF changes common across psychiatric disorders, we capitalized upon a sample of 1042 youths (ages 11-23 years) who completed cross-sectional imaging as part of the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort. CBF at rest was quantified on a voxelwise basis using arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI at 3T. A dimensional measure of psychopathology was constructed using a bifactor model of item-level data from a psychiatric screening interview, which delineated four factors (fear, anxious-misery, psychosis and behavioral symptoms) plus a general factor: overall psychopathology. Overall psychopathology was associated with elevated perfusion in several regions including the right dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and left rostral ACC. Furthermore, several clusters were associated with specific dimensions of psychopathology. Psychosis symptoms were related to reduced perfusion in the left frontal operculum and insula, whereas fear symptoms were associated with less perfusion in the right occipital/fusiform gyrus and left subgenual ACC. Follow-up functional connectivity analyses using resting-state functional MRI collected in the same participants revealed that overall psychopathology was associated with decreased connectivity between the dorsal ACC and bilateral caudate. Together, the results of this study demonstrate common and dissociable CBF abnormalities across neuropsychiatric disorders in youth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Flamez B, Sheperis C. Diagnosing and treating children and adolescents: A guide for mental health professionals. New Jersey: John Wiley and Son’s; 2016.
-
- Angold A, Costello EJ, Erkanli A. Comorbidity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 1999;40:57–87. - PubMed
-
- Ellison-Wright I, Bullmore E. Anatomy of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Schizophr Res. 2010;117:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

