An alternate mode of oligomerization for E. coli SecA
- PMID: 28924213
- PMCID: PMC5603524
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11648-5
An alternate mode of oligomerization for E. coli SecA
Abstract
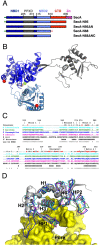
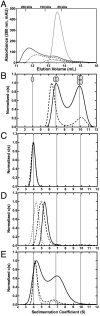
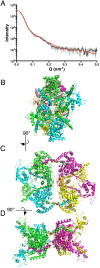
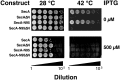
SecA is the ATPase of preprotein translocase. SecA is a dimer in solution and changes in its oligomeric state may function in preprotein translocation. The SecA-N68 construct, in which the C-terminal helical domains of SecA are deleted, was used to investigate the mechanism of SecA oligomerization. SecA-N68 is in equilibrium between monomers, dimers, and tetramers. Subunit interactions in the SecA-N68 tetramer are mediated entirely by unstructured regions at its N- and C-termini: when the termini are deleted to yield SecA-N68∆NC, the construct is completely monomeric. This monomeric construct yielded crystals diffracting to 2.6 Å that were used to solve the structure of SecA-N68, including the "preprotein crosslinking domain" (PPXD) that was missing from previous E. coli SecA structures. The SecA-N68 structure was combined with small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) data to construct a model of the SecA-N68 tetramer that is consistent with the essential roles of the extreme N- and C-termini in oligomerization. This mode of oligomerization, which depends on binding of the extreme N-terminus to the DEAD motor domains, NBD1 and NBD2, was used to model a novel parallel and flexible SecA solution dimer that agrees well with SAXS data.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ATPase domain of SecA can form a tetramer in solution.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jan 25;315(4):831-43. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5279. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11812151
-
Characterization of a polypeptide-binding site in the DEAD Motor of the SecA ATPase.FEBS Lett. 2017 Oct;591(20):3378-3390. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12832. Epub 2017 Sep 12. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28862749
-
Analysis of SecA dimerization in solution.Biochemistry. 2014 May 20;53(19):3248-60. doi: 10.1021/bi500348p. Epub 2014 May 9. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24786965 Free PMC article.
-
SecA: a tale of two protomers.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jun 1;76(5):1070-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07176.x. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20444093 Review.
-
SecA - a multidomain and multitask bacterial export protein.Acta Biochim Pol. 2021 Aug 31;68(3):427-436. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5761. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021. PMID: 34463460 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the substrate-engaged SecA-SecY protein translocation machine.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 28;10(1):2872. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10918-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31253804 Free PMC article.
-
Direct visualization of the E. coli Sec translocase engaging precursor proteins in lipid bilayers.Sci Adv. 2019 Jun 12;5(6):eaav9404. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav9404. eCollection 2019 Jun. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31206019 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

