Implication of the glutamate-cystine antiporter xCT in schizophrenia cases linked to impaired GSH synthesis
- PMID: 28924227
- PMCID: PMC5603608
- DOI: 10.1038/s41537-017-0035-3
Implication of the glutamate-cystine antiporter xCT in schizophrenia cases linked to impaired GSH synthesis
Abstract
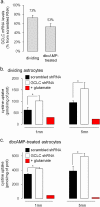
xCT is the specific chain of the cystine/glutamate antiporter, which is widely reported to support anti-oxidant defenses in vivo. xCT is therefore at the crossroads between two processes that are involved in schizophrenia: oxidative stress and glutamatergic neurotransmission. But data from human studies implicating xCT in the illness and clarifying the upstream mechanisms of xCT imbalance are still scarce. Low glutathione (GSH) levels and genetic risk in GCLC (Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Catalytic subunit), the gene of limiting synthesizing enzyme for GSH, are both associated with schizophrenia. In the present study, we aimed at determining if xCT regulation by the redox system is involved in schizophrenia pathophysiology. We assessed whether modulating GCLC expression impact on xCT expression and activity (i) in fibroblasts from patients and controls with different GCLC genotypes which are known to affect GCLC regulation and GSH levels; (ii) in rat brain glial cells, i.e., astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, with a knock-down of GCLC. Our results highlight that decreased GCLC expression leads to an upregulation of xCT levels in patients' fibroblasts as well as in astrocytes. These results support the implication of xCT dysregulation in illness pathophysiology and further indicate that it can result from redox changes. Additionally, we showed that these anomalies may already take place at early stages of psychosis and be more prominent in a subgroup of patients with GCLC high-risk genotypes. These data add to the existing evidence identifying the inflammatory/redox systems as important targets to treat schizophrenia already at early stages.
Schizophrenia: ANTIOXIDANT DEFICIT INCREASES A KEY NEUROTRANSMITTER TRANSPORTER: Deficit of antioxidant synthesis in schizophrenia leads to oxidative stress and changes in neurotransmitter transporter. Led by Kim Do, a team of researchers from Lausanne University in Switzerland investigated the role of the cell-surface transport protein xCT in schizophrenia. They found that an enzyme responsible for antioxidant production is disturbed in patients. This leads to decreased antioxidant levels and consequently to oxidative stress-i.e. the accumulation of reactive oxygen molecules, damaging the cells component and impairing cell functioning-which in turn affects the functioning of the antioxidant pathway, including xCT. xCT, which exports the neurotransmitter glutamate, is thus overproduced in schizophrenia. The resulting increase of neurotransmitter activity, alongside the increase in oxidative stress, is thought to play a major role in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, including at early stages of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The proteasome inhibitor lactacystin enhances GSH synthesis capacity by increased expression of antioxidant components in an Nrf2-independent, but p38 MAPK-dependent manner in rat colorectal carcinoma cells.Free Radic Res. 2016;50(1):1-13. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1100730. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Free Radic Res. 2016. PMID: 26530909
-
Expression of xCT and activity of system xc(-) are regulated by NRF2 in human breast cancer cells in response to oxidative stress.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 25827424 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Polymorphism Associated Prefrontal Glutathione and Its Coupling With Brain Glutamate and Peripheral Redox Status in Early Psychosis.Schizophr Bull. 2016 Sep;42(5):1185-96. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbw038. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Schizophr Bull. 2016. PMID: 27069063 Free PMC article.
-
The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Feb 10;18(5):522-55. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4391. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22667998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Oxidative stress involvement in schizophrenia pathophysiology: a review].Encephale. 2006 Mar-Apr;32(2 Pt 1):244-52. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76151-6. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 16910626 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Mn Inhibits GSH Synthesis via Downregulation of Neuronal EAAC1 and Astrocytic xCT to Cause Oxidative Damage in the Striatum of Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Aug 30;2018:4235695. doi: 10.1155/2018/4235695. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30228854 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated methylome and phenome study of the circulating proteome reveals markers pertinent to brain health.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 9;13(1):4670. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32319-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35945220 Free PMC article.
-
Structural investigation of human cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc - (Sxc -) using homology modeling and molecular dynamics.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 1;9:1064199. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1064199. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36533083 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Glutamate Homeostasis in the Brain of Rat Offspring Induced by Prenatal and Early Postnatal Exposure to Maternal High-Sugar Diet.Nutrients. 2022 May 24;14(11):2184. doi: 10.3390/nu14112184. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35683984 Free PMC article.
-
Central Oxidative Stress and Early Vocational Outcomes in First Episode Psychosis: A 7-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study of Glutathione.Schizophr Bull. 2022 Jun 21;48(4):921-930. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbac012. Schizophr Bull. 2022. PMID: 35307736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannai S. Exchange of cystine and glutamate across plasma membrane of human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:2256–2263. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

