Pharmacological inhibition of CaMKK2 with the selective antagonist STO-609 regresses NAFLD
- PMID: 28924233
- PMCID: PMC5603587
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12139-3
Pharmacological inhibition of CaMKK2 with the selective antagonist STO-609 regresses NAFLD
Abstract
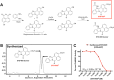
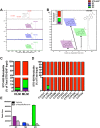
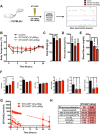
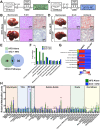
Binding of calcium to its intracellular receptor calmodulin (CaM) activates a family of Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinases. CaMKK2 (Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase kinase 2) is a central member of this kinase family as it controls the actions of a CaMK cascade involving CaMKI, CaMKIV or AMPK. CaMKK2 controls insulin signaling, metabolic homeostasis, inflammation and cancer cell growth highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for a variety of diseases. STO-609 is a selective, small molecule inhibitor of CaMKK2. Although STO-609 has been used extensively in vitro and in cells to characterize and define new mechanistic functions of CaMKK2, only a few studies have reported the in vivo use of STO-609. We synthesized functional STO-609 and assessed its pharmacological properties through in vitro (kinase assay), ex vivo (human liver microsomes) and in vivo (mouse) model systems. We describe the metabolic processing of STO-609, its toxicity, pharmacokinetics and bioavailability in a variety of mouse tissues. Utilizing these data, we show STO-609 treatment to inhibit CaMKK2 function confers protection against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. These data provide a valuable resource by establishing criteria for use of STO-609 to inhibit the in vivo functions of CaMKK2 and demonstrate its utility for treating metabolically-related hepatic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using the fluorescent properties of STO-609 as a tool to assist structure-function analyses of recombinant CaMKK2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jul 22;476(2):102-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.045. Epub 2016 May 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27178209
-
Inhibition of CaMKK2 reverses age-associated decline in bone mass.Bone. 2015 Jun;75:120-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.01.021. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25724145 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 stimulates osteoblast formation and inhibits osteoclast differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Jul;28(7):1599-610. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1890. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23408651 Free PMC article.
-
The Ca(2+)/Calmodulin/CaMKK2 Axis: Nature's Metabolic CaMshaft.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Oct;27(10):706-718. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27449752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2: roles in signaling and pathophysiology.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 14;287(38):31658-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.356485. Epub 2012 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22778263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The rheumatoid arthritis drug auranofin lowers leptin levels and exerts antidiabetic effects in obese mice.Cell Metab. 2022 Dec 6;34(12):1932-1946.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.019. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Cell Metab. 2022. PMID: 36243005 Free PMC article.
-
CAMKK2-AMPK axis endows dietary calcium and phosphorus levels with regulatory effects on lipid metabolism in weaned piglets.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 5;15(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01061-0. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39098913 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid dimethyl ether alleviates alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis via microRNA-378b-mediated CaMKK2-AMPK pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):11122-11136. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2060586. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35481488 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen Receptor-CaMKK2 Axis in Prostate Cancer and Bone Microenvironment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jun 18;9:335. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00335. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29967592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hinge Binder Scaffold Hopping Identifies Potent Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Kinase 2 (CAMKK2) Inhibitor Chemotypes.J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 12;64(15):10849-10877. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02274. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34264658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carafoli, E. A. K., C. B. Calcium as a cellular regulator. Vol. xiii 642 (Oxford University Press, 1999).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

