LncRNA AFAP1-AS Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate RAP1B Expression by sponging miR-181a in the HSCR
- PMID: 28924375
- PMCID: PMC5599927
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.18392
LncRNA AFAP1-AS Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate RAP1B Expression by sponging miR-181a in the HSCR
Erratum in
-
Erratum: LncRNA AFAP1-AS Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate RAP1B Expression by sponging miR-181a in the HSCR: Erratum.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Oct 2;15(13):1472. doi: 10.7150/ijms.29742. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30443167 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have recently emerged as important regulators in a broad spectrum of cellular processes including development and disease. Despite the known engagement of the AFAP1-AS in several human diseases, its biological function in Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) remains elusive. Methods: We used qRT-PCR to detect the relative expression of AFAP1-AS in 64 HSCR bowel tissues and matched normal intestinal tissues. The effects of AFAP1-AS on cell proliferation, migration, cell cycle, apoptosis and cytoskeletal organization were evaluated using CCK-8, transwell assay, flow cytometer analysis and immunofluorescence, in 293T and SH-SY5Y cell lines, respectively. Moreover, the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) activity of AFAP1-AS on miR-181a was investigated via luciferase reporter assay and immunoblot analysis. Results: Aberrant inhibition of AFAP1-AS was observed in HSCR tissues. Knockdown of AFAP1-AS in 293T and SH-SY5Y cells suppressed cell proliferation, migration, and induced the loss of cell stress filament integrity, possibly due to AFAP1-AS sequestering miR-181a in HSCR cells. Furthermore, AFAP1-AS could down-regulate RAP1B via its competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) activity on miR-181a. Conclusions: These findings suggest that aberrant expression of lncRNA AFAP1-AS, a ceRNA of miR-181a, may involve in the onset and progression of HSCR by augmenting the miR-181a target gene, RAP1B.
Keywords: AFAP1-AS; Competing endogenous RNA; Hirschsprung disease; miR-181a..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
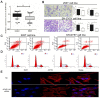

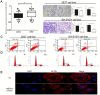

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA LOC100507600 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate BMI1 expression by sponging miR128-1-3p in Hirschsprung's disease.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(4):459-467. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1403688. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29429387 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA FAL1 functions as a ceRNA to antagonize the effect of miR-637 on the down-regulation of AKT1 in Hirschsprung's disease.Cell Prolif. 2018 Oct;51(5):e12489. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12489. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 30062828 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the lncRNA AFAP1-AS1/microRNA-195/E2F3 axis in proliferation and migration of enteric neural crest stem cells of Hirschsprung's disease.Exp Physiol. 2020 Nov;105(11):1939-1949. doi: 10.1113/EP088780. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Exp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32959905
-
The role of long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 in human malignant tumors.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Oct;214(10):1524-1531. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.08.014. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30173945 Review.
-
Role of miR-181a in the process of apoptosis of multiple malignant tumors: A literature review.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018 Feb;27(2):263-270. doi: 10.17219/acem/66842. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29521071 Review.
Cited by
-
AFAP1-AS1: a rising star among oncogenic long non-coding RNAs.Sci China Life Sci. 2021 Oct;64(10):1602-1611. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1874-6. Epub 2021 May 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33999309 Review.
-
MicroRNA regulation of enteric nervous system development and disease.Trends Neurosci. 2025 Apr;48(4):268-282. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2025.02.004. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Trends Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40089421 Review.
-
Identifying the potential transcriptional regulatory network in Hirschsprung disease by integrated analysis of microarray datasets.World J Pediatr Surg. 2023 Apr 17;6(2):e000547. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2022-000547. eCollection 2023. World J Pediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 37082700 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Prediction for Network-Based Integrative Multi-Omics Expression Data Analysis in Hirschsprung Disease.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 30;14(2):164. doi: 10.3390/biom14020164. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397401 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of New Potential LncRNA Biomarkers in Hirschsprung Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 2;21(15):5534. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155534. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32748823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borrego S, Ruiz-Ferrer M, Fernandez RM, Antinolo G. Hirschsprung's disease as a model of complex genetic etiology. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28:1117–36. - PubMed
-
- Spouge D, Baird PA. Hirschsprung disease in a large birth cohort. Teratology. 1985;32:171–7. - PubMed
-
- McKeown SJ, Stamp L, Hao MM, Young HM. Hirschsprung disease: a developmental disorder of the enteric nervous system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013;2:113–29. - PubMed
-
- Tang W, Tang J, Qin J, Geng Q, Zhou Z, Li B. et al. Involvement of down-regulated E2F3 in Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48:813–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

