Spatiotemporal Expression of Wnt/β-catenin Signaling during Morphogenesis and Odontogenesis of Deciduous Molar in Miniature Pig
- PMID: 28924388
- PMCID: PMC5599912
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.20905
Spatiotemporal Expression of Wnt/β-catenin Signaling during Morphogenesis and Odontogenesis of Deciduous Molar in Miniature Pig
Abstract
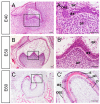
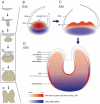
The canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has been shown to play essential roles in tooth initiation and early tooth development. However, the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cusp patterning and crown calcification in large mammals are largely unknown. In our previous study, miniature pigs were used as the animal model due to the similarity of tooth anatomy and replacement pattern between miniature pig and human. Dynamic gene expression of third deciduous molar (DM3) in miniature pig at early stages was profiled using microarray method and expression of Wnt genes was significantly correlate with odontogenesis. In the present study, dynamic expression patterns of Wnt/β-catenin signaling genes of DM3 at cap, early bell and late bell (secretory) stage were identified. We found that Lef1 and Axin2 were expressed in the enamel knot and underlying mesenchyme regions. Meanwhile, Dkk1 was expressed in the peripheral and lower parts of dental papilla, thus forming the potential Wnt signaling gradient. We also found that β-Catenin, Axin2 and Lef1 were expressed strongly in undifferentiated cells of the inner enamel epithelium (IEE), but weakly in differentiated ameloblasts. Furthermore, we found that both Wnt signaling read-out gene Lef1 and the inhibitor Dkk1 were co-expressed in the pre-odontoblasts. In conclusion, the spatiotemporal distribution and potential gradient of Wnt signaling may contribute to cusp patterning and crown calcification. These data may yield insight into future study of precise control of crown morphogenesis and regeneration in large mammals.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; development; miniature pig; tooth.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gene expression of beta-catenin is up-regulated in inner dental epithelium and enamel knots during molar tooth morphogenesis in the mouse.Cell Tissue Res. 2006 Jul;325(1):197-201. doi: 10.1007/s00441-005-0136-6. Epub 2006 Mar 21. Cell Tissue Res. 2006. PMID: 16550360
-
Homeobox protein MSX-1 inhibits expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2, bone morphogenetic protein 4, and lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 via Wnt/β-catenin signaling to prevent differentiation of dental mesenchymal cells during the late bell stage.Eur J Oral Sci. 2018 Feb;126(1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/eos.12390. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018. PMID: 29148101
-
Spatiotemporal Expression Patterns of Critical Genes Involved in FGF Signaling During Morphogenesis and Odontogenesis of Deciduous Molars in Miniature Pigs.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jan 1;19(1):132-141. doi: 10.7150/ijms.61798. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34975307 Free PMC article.
-
Enamel knots as signaling centers linking tooth morphogenesis and odontoblast differentiation.Adv Dent Res. 2001 Aug;15:14-8. doi: 10.1177/08959374010150010401. Adv Dent Res. 2001. PMID: 12640732 Review.
-
Tooth morphogenesis and pattern of odontoblast differentiation.Connect Tissue Res. 2003;44 Suppl 1:167-70. Connect Tissue Res. 2003. PMID: 12952192 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphogenesis of fungiform papillae in developing miniature pigs.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 22;10(3):e24953. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24953. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38314265 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental basis of natural tooth shape variation in cichlid fishes.Naturwissenschaften. 2025 Jan 27;112(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s00114-025-01964-6. Naturwissenschaften. 2025. PMID: 39869142 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted frizzled-related protein 2 promotes the osteo/odontogenic differentiation and paracrine potentials of stem cells from apical papilla under inflammation and hypoxia conditions.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jan;53(1):e12694. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12694. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31568642 Free PMC article.
-
Tooth Regeneration: Insights from Tooth Development and Spatial-Temporal Control of Bioactive Drug Release.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020 Feb;16(1):41-55. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-09940-0. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020. PMID: 31834583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Detection for Runs of Homozygosity in Baoshan Pigs Using Whole Genome Resequencing.Genes (Basel). 2024 Feb 12;15(2):233. doi: 10.3390/genes15020233. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tucker A, Sharpe P. The cutting-edge of mammalian development; how the embryo makes teeth. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:499–508. - PubMed
-
- Jernvall J, Thesleff I. Reiterative signaling and patterning during mammalian tooth morphogenesis. Mech Dev. 2000;92:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

