Identification and analysis of CYP450 genes from transcriptome of Lonicera japonica and expression analysis of chlorogenic acid biosynthesis related CYP450s
- PMID: 28924501
- PMCID: PMC5600180
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3781
Identification and analysis of CYP450 genes from transcriptome of Lonicera japonica and expression analysis of chlorogenic acid biosynthesis related CYP450s
Abstract
Background: Lonicera japonica is an important medicinal plant that has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for thousands of years. The pharmacological activities of L. japonica are mainly due to its rich natural active ingredients, most of which are secondary metabolites. CYP450s are a large, complex, and widespread superfamily of proteins that participate in many endogenous and exogenous metabolic reactions, especially secondary metabolism. Here, we identified CYP450s in L. japonica transcriptome and analyzed CYP450s that may be involved in chlorogenic acid (CGA) biosynthesis.
Methods: The recent availability of L. japonica transcriptome provided opportunity to identify CYP450s in this herb. BLAST based method and HMM based method were used to identify CYP450s in L. japonica transcriptome. Then, phylogenetic analysis, conserved motifs analysis, GO annotation, and KEGG annotation analyses were conducted to characterize the identified CYP450s. qRT-PCR was used to explore expression patterns of five CGA biosynthesis related CYP450s.
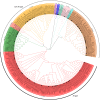
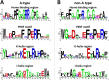
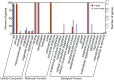
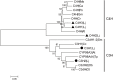
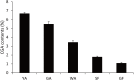
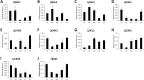
Results: In this study, 151 putative CYP450s with complete cytochrome P450 domain, which belonged to 10 clans, 45 families and 76 subfamilies, were identified in L. japonica transcriptome. Phylogenetic analysis classified these CYP450s into two major branches, A-type (47%) and non-A type (53%). Both types of CYP450s had conserved motifs in L. japonica. The differences of typical motif sequences between A-type and non-A type CYP450s in L. japonica were similar with other plants. GO classification indicated that non-A type CYP450s participated in more molecular functions and biological processes than A-type. KEGG pathway annotation totally assigned 47 CYP450s to 25 KEGG pathways. From these data, we cloned two LjC3Hs (CYP98A subfamily) and three LjC4Hs (CYP73A subfamily) that may be involved in biosynthesis of CGA, the major ingredient for pharmacological activities of L. japonica. qRT-PCR results indicated that two LjC3Hs exhibited oppositing expression patterns during the flower development and LjC3H2 exhibited a similar expression pattern with CGA concentration measured by HPLC. The expression patterns of three LjC4Hs were quite different and the expression pattern of LjC4H3 was quite similar with that of LjC3H1.
Discussion: Our results provide a comprehensive identification and characterization of CYP450s in L. japonica. Five CGA biosynthesis related CYP450s were cloned and their expression patterns were explored. The different expression patterns of two LjC3Hs and three LjC4Hs may be due to functional divergence of both substrate and catalytic specificity during plant evolution. The co-expression pattern of LjC3H1 and LjC4H3 strongly suggested that they were under coordinated regulation by the same transcription factors due to same cis elements in their promoters. In conclusion, this study provides insight into CYP450s and will effectively facilitate the research of biosynthesis of CGA in L. japonica.
Keywords: C3H; C4H; CGA biosynthesis; CYP450; Lonicera japonica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of buds and leaves using 454 pyrosequencing to discover genes associated with the biosynthesis of active ingredients in Lonicera japonica Thunb.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 25;8(4):e62922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062922. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23638167 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome assembly and characterization of nine tissues of Lonicera japonica to identify potential candidate genes involved in chlorogenic acid, luteolosides, and secoiridoid biosynthesis pathways.J Nat Med. 2017 Jan;71(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s11418-016-1041-x. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 27629269 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated metabolic profiling and transcriptome analysis of Lonicera japonica flowers for chlorogenic acid, luteolin and endogenous hormone syntheses.Gene. 2023 Dec 20;888:147739. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147739. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Gene. 2023. PMID: 37633535
-
Regulatory mechanisms and biosynthesis of chlorogenic acid in Lonicera japonica: insights from tissue culture and inducer treatments.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Apr 24;16:1567140. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1567140. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40343127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the cytochrome P450 superfamily in the skin.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Apr 15;26:e15. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.5. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38621674 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, comparative analysis and functional roles in flavonoid biosynthesis of cytochrome P450 superfamily in pear (Pyrus spp.).BMC Genom Data. 2023 Oct 3;24(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12863-023-01159-w. BMC Genom Data. 2023. PMID: 37789271 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of Lonicera japonica Thunb. during flower development as revealed by comprehensive analysis of transcription factors.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 May 14;19(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1803-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31088368 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and evolution of cytochrome P450s of Jacobaea vulgaris and Jacobaea aquatica.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jul 20;20(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02532-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32689941 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Lonicera japonica and a proposed floral organ identity model.BMC Genomics. 2023 Aug 8;24(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09509-9. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37553575 Free PMC article.
-
Research Advances in the Synthesis, Metabolism, and Function of Chlorogenic Acid.Foods. 2025 May 28;14(11):1914. doi: 10.3390/foods14111914. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509442 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bi C, Chen F, Jackson L, Gill BS, Li W. Expression of lignin biosynthetic genes in wheat during development and upon infection by fungal pathogens. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter. 2011;29:149–161. doi: 10.1007/s11105-010-0219-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

