Ex vivo tissue imaging for radiology-pathology correlation: a pilot study with a small bore 7-T MRI in a rare pigmented ganglioglioma exhibiting complex MR signal characteristics associated with melanin and hemosiderin
- PMID: 28924575
- PMCID: PMC5596201
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.3.036001
Ex vivo tissue imaging for radiology-pathology correlation: a pilot study with a small bore 7-T MRI in a rare pigmented ganglioglioma exhibiting complex MR signal characteristics associated with melanin and hemosiderin
Abstract
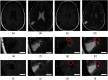
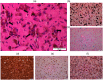
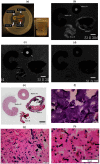
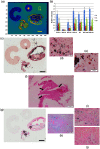
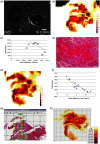
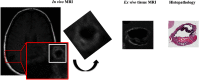
To advance magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technologies further for in vivo tissue characterization with histopathologic validation, we investigated the feasibility of ex vivo tissue imaging of a surgically removed human brain tumor as a comprehensive approach for radiology-pathology correlation in histoanatomically identical fashion in a rare case of pigmented ganglioglioma with complex paramagnetic properties. Pieces of surgically removed ganglioglioma, containing melanin and hemosiderin pigments, were imaged with a small bore 7-T MRI scanner to obtain T1-, T2-, and T2*-weighted image and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Corresponding histopathological slides were prepared for routine hematoxylin and eosin stain and special stains for melanin and iron/hemosiderin to correlate with MRI signal characteristics. Furthermore, mean diffusivity (MD) maps were generated from DTI data and correlated with cellularity using image analysis. While the presence of melanin was difficult to interpret in in vivo MRI with certainty due to concomitant hemosiderin pigments and calcium depositions, ex vivo tissue imaging clearly demonstrated pieces of tissue exhibiting the characteristic MR signal pattern for melanin with pathologic confirmation in a histoanatomically identical location. There was also concordant correlation between MD and cellularity. Although it is still in an initial phase of development, ex vivo tissue imaging is a promising approach, which offers radiology-pathology correlation in a straightforward and comprehensive manner.
Keywords: ex vivo tissue imaging; melanin-associated magnetic resonance imaging signal; pigmented ganglioglioma; radiology–pathology correlation; small bore 7-T magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ex Vivo MR Histology and Cytometric Feature Mapping Connect Three-dimensional in Vivo MR Images to Two-dimensional Histopathologic Images of Murine Sarcomas.Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2021 May;3(3):e200103. doi: 10.1148/rycan.2021200103. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34018846 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial metastatic melanoma: correlation between MR imaging characteristics and melanin content.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995 Dec;165(6):1503-12. doi: 10.2214/ajr.165.6.7484597. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995. PMID: 7484597
-
Ultra-high resolution and multi-shell diffusion MRI of intact ex vivo human brains using kT-dSTEAM at 9.4T.Neuroimage. 2019 Nov 15;202:116087. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116087. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31408716
-
Diffusion-weighted MR of the brain: methodology and clinical application.Radiol Med. 2005 Mar;109(3):155-97. Radiol Med. 2005. PMID: 15775887 Review. English, Italian.
-
Iron-containing pathologies of the spleen: magnetic resonance imaging features with pathologic correlation.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Mar;46(3):1016-1026. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02709-x. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 32915270 Review.
Cited by
-
Matching ex vivo MRI With Iron Histology: Pearls and Pitfalls.Front Neuroanat. 2019 Jul 3;13:68. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2019.00068. eCollection 2019. Front Neuroanat. 2019. PMID: 31333421 Free PMC article.
-
Tensor image registration library: Deformable registration of stand-alone histology images to whole-brain post-mortem MRI data.Neuroimage. 2023 Jan;265:119792. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119792. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Neuroimage. 2023. PMID: 36509214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuda K. M., et al. , “Microscopic resolution imaging and proteomics correlation at histogeographically identical location: point by point correlation between ex vivo tissue imaging with high field MRI and multiplex tissue immunoblotting for proteomics profiling,” Proc. SPIE 7626, 76262B (2010).10.1117/12.854966 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

