GH Supplementation Effects on Cardiovascular Risk in GH Deficient Adult Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 28925898
- PMCID: PMC5925873
- DOI: 10.2174/1871530317666170919121729
GH Supplementation Effects on Cardiovascular Risk in GH Deficient Adult Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and objective: The current meta-analysis aims at evaluating whether the existing clinical evidence may ascertain the effects of growth hormone (GH) replacement therapy on cardiovascular risk, both in isolated GH deficiency (GHD) and in compensated panhypopituitarism including GH deficit.
Methods: Original articles published from 1991 to 2015 were searched on Medline (Pubmed). Among an overall number of 181 potentially suitable studies, 24 fulfilled the selection criteria and were included in the analysis. Data aggregation was carried out through the calculation of the absolute risk reduction. The meta-analysis was then conducted by means of a fixed-effects model, according to the heterogeneity test (Chi-square statistic).
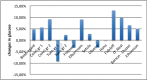
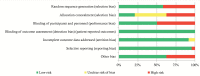
Results: Fat-free mass (FFM) increase and fat mass (FM) reduction were found, together with a C-LDL reduction, a wide variation in glycaemia and a neutral effect on glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and blood pressure. These effects were valid both for isolated GHD patients and for those with compensated panhypopituitarism. The global outcome D showed a nonsignificant reduction of the overall cardiovascular risk (0.53; 95% C.I. -1.23, 2.85).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis shows no signnificatly positive trend in cardiovascular risk after both short and long-term GH supplementation therapy in adult GHD patients. However, a reduction of LDL cholesterol levels has been found. No differences were found between isolated GHD participants and those affected by panhypopituitarism well compensated since at least 3 months.
Keywords: GH deficit; GH supplementation; body composition; cardiovascular risk; cardiovascular risk factors; panhypopituitarism.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Treatments for seizures in catamenial (menstrual-related) epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 16;9(9):CD013225. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013225.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34528245 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking cessation for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 8;8(8):CD014936. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014936.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35938889 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed-dose combination therapy for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 6;3(3):CD009868. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009868.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28263370 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A 2024 Update on Growth Hormone Deficiency Syndrome in Adults: From Guidelines to Real Life.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 12;13(20):6079. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206079. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of adult growth hormone deficiency and replacement therapy on the cardiometabolic risk profile.Pituitary. 2022 Apr;25(2):211-228. doi: 10.1007/s11102-022-01207-1. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Pituitary. 2022. PMID: 35106704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF-1 and cardiovascular disease.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2019 Apr;45:6-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2019. PMID: 30735831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term Safety of Growth Hormone in Adults With Growth Hormone Deficiency: Overview of 15 809 GH-Treated Patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jun 16;107(7):1906-1919. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac199. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35368070 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of long-term growth hormone replacement on glucose metabolism in adults with growth hormone deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pituitary. 2021 Feb;24(1):130-142. doi: 10.1007/s11102-020-01079-3. Pituitary. 2021. PMID: 32888174
References
-
- Borson-Chazot F., Serusclat A., Kalfallah Y., Ducottet X., Sassolas G., Bernard S., Labrousse F., Pastene J., Sassolas A., Roux Y., Berthezène F. Decrease in carotid intima-media thickness after one year growth hormone (GH) treatment in adults with GH deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999;84(4):1329–1333. - PubMed
-
- Allen D.B., Backeljauw P., Bidlingmaier M., Biller B.M., Boguszewski M., Burman P., Butler G., Chihara K., Christiansen J., Cianfarani S., Clayton P., Clemmons D., Cohen P., Darendeliler F., Deal C., Dunger D., Erfurth E.M., Fuqua J.S., Grimberg A., Haymond M., Higham C., Ho K., Hoffman A.R., Hokken-Koelega A., Johannsson G., Juul A., Kopchick J., Lee P., Pollak M., Radovick S., Robison L., Rosenfeld R., Ross R.J., Savendahl L., Saenger P., Toft Sorensen H., Stochholm K., Strasburger C., Swerdlow A., Thorner M. GH safety workshop position paper: a critical appraisal of recombinant human GH therapy in children and adults. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016;174(2):1–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albertsson-Wikland K., Martensson A., Savendahl L., Niklasson A., Bang P., Dahlgren J., Gustafsson J., Kriström B., Norgren S., Pehrsson N.G., Odén A. Mortality is not increased in recombinant human growth hormone-treated patients when adjusting for birth characteristics. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;101(5):2149–2159. - PubMed
-
- Vasan R.S., Sullivan L.M., D’Agostino R.B., Roubenoff R., Harris T., Sawyer D.B., Levy D., Wilson P.W. Serum insulin-like growth factor I and risk for heart failure in elderly individuals without a previous myocardial infarction: the Framingham Heart Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003;139(8):642–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases