Lower mitochondrial DNA and altered mitochondrial fuel metabolism in HIV-exposed uninfected infants in Cameroon
- PMID: 28926411
- PMCID: PMC5680102
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001647
Lower mitochondrial DNA and altered mitochondrial fuel metabolism in HIV-exposed uninfected infants in Cameroon
Abstract
Objective: Evaluate blood mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content in HIV/antiretroviral-exposed uninfected (HEU) vs. HIV-unexposed uninfected (HUU) infants and investigate differences in mitochondrial-related metabolites by exposure group.
Design: We enrolled a prospective cohort of HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected pregnant woman/infant pairs in Cameroon.
Methods: Dried blood spot mtDNA : nuclear DNA ratio was measured by monochrome multiplex quantitative polymerase chain reaction in HEU infants exposed to in-utero antiretrovirals and postnatal zidovudine (HEU-Z) or nevirapine (HEU-N), and in HUU infants at 6 weeks of life. Acylcarnitines and branch-chain amino acids (BCAAs) were measured via tandem mass spectrometry and consolidated into seven uncorrelated components using principal component analysis. Linear regression models were fit to assess the association between in-utero/postnatal HIV/antiretroviral exposure and infant mtDNA, adjusting for confounders and principal component analysis-derived acylcarnitine/BCAA component scores.
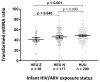
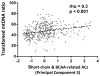
Results: Of 364 singleton infants, 38 were HEU-Z, 117 HEU-N, and 209 HUU. Mean mtDNA content was lowest in HEU-Z infants (140 vs. 160 in HEU-N vs. 174 in HUU, P = 0.004). After adjusting for confounders, HEU-Z infants remained at increased risk for lower mtDNA content compared with HUU infants (β: -4.46, P = 0.045), whereas HEU-N infants did not, compared with HUU infants (β: -1.68, P = 0.269. Furthermore, long-chain acylcarnitines were associated with lower (β: -2.35, P = 0.002) and short-chain and BCAA-related acylcarnitines were associated with higher (β: 2.96, P = 0.001) mtDNA content.
Conclusion: Compared with HUU infants, HEU infants receiving postnatal zidovudine appear to be at increased risk for decreased blood mtDNA content which may be associated with altered mitochondrial fuel utilization in HEU-Z infants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lower Preprandial Insulin and Altered Fuel Use in HIV/Antiretroviral-Exposed Infants in Cameroon.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Sep;100(9):3260-9. doi: 10.1210/JC.2015-2198. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26133363 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct cord blood C-peptide, adipokine, and lipidomic signatures by in utero HIV exposure.Pediatr Res. 2022 Jul;92(1):233-241. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01705-1. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34446848 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte Telomere Length at Birth and During the Early Life of Children Exposed to but Uninfected With HIV After In Utero Exposure to Antiretrovirals.J Infect Dis. 2018 Feb 14;217(5):710-720. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix618. J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29228317 Free PMC article.
-
Health and survival of HIV perinatally exposed but uninfected children born to HIV-infected mothers.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016 Sep;11(5):465-476. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000300. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016. PMID: 27716731 Review.
-
A Meta-analysis Assessing Diarrhea and Pneumonia in HIV-Exposed Uninfected Compared With HIV-Unexposed Uninfected Infants and Children.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Sep 1;82(1):1-8. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002097. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31408450 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human immunodeficiency virus and antiretroviral therapy-mediated immune cell metabolic dysregulation in children born to HIV-infected women: potential clinical implications.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 7;14:1182217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1182217. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37350953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral Blood Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number Obtained From Genome-Wide Genotype Data Is Associated With Neurocognitive Impairment in Persons With Chronic HIV Infection.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Apr 1;80(4):e95-e102. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001930. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019. PMID: 30531306 Free PMC article.
-
Association of In Utero HIV Exposure With Obesity and Reactive Airway Disease in HIV-Negative Adolescents and Young Adults.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020 Feb 1;83(2):126-134. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002235. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020. PMID: 31738195 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-exposed-uninfected infants have increased inflammation and monocyte activation.AIDS. 2019 Apr 1;33(5):845-853. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002128. AIDS. 2019. PMID: 30649056 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Parameters in Blood of Infants Receiving Lopinavir/Ritonavir or Lamivudine Prophylaxis to Prevent Breastfeeding Transmission of HIV-1.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 14;9(9):2972. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092972. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32937988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanche S, Tardieu M, Rustin P, Slama A, Barret B, Firtion G, et al. Persistent mitochondrial dysfunction and perinatal exposure to antiretroviral nucleoside analogues. Lancet. 1999;354(9184):1084–1089. - PubMed
-
- Poirier MC, Divi RL, Al-Harthi L, Olivero OA, Nguyen V, Walker B, et al. Long-term mitochondrial toxicity in HIV-uninfected infants born to HIV-infected mothers. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;33(2):175–183. - PubMed
-
- Divi RL, Walker VE, Wade NA, Nagashima K, Seilkop SK, Adams ME, et al. Mitochondrial damage and DNA depletion in cord blood and umbilical cord from infants exposed in utero to Combivir. AIDS. 2004;18(7):1013–1021. - PubMed
-
- Cote HC, Raboud J, Bitnun A, Alimenti A, Money DM, Maan E, et al. Perinatal exposure to antiretroviral therapy is associated with increased blood mitochondrial DNA levels and decreased mitochondrial gene expression in infants. J Infect Dis. 2008;198(6):851–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

