Inhibition of LHX2 by miR-124 suppresses cellular migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 28927097
- PMCID: PMC5587980
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6607
Inhibition of LHX2 by miR-124 suppresses cellular migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
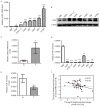
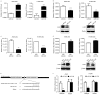
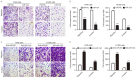
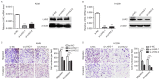
Downregulated microRNA (miR)-124 is common in numerous types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). A previous study by the authors demonstrated that LIM-homeobox domain 2 (LHX2) was upregulated and promoted cell growth in NSCLC. However, whether LHX2 affects the migratory and invasive abilities of NSCLC cells and the association of LHX2 with miR-124 remains unclear. The present study revealed that miR-124 expression was frequently decreased in human NSCLC cells and tissues and negatively correlated with LHX2 expression, which was increased in NSCLC cells and tissues. Furthermore, the transfection of miR-124 mimic significantly inhibited endogenous expression of LHX2 mRNA and protein in A549 and H1299 cells, and miR-124 inhibitor promoted LHX2 expression. Of note, overexpression of miR-124 in A549 and H1299 cells attenuated cellular migratory and invasive abilities, and this was observed in LHX2-silenced A549 and H1299 cells. Knockdown of miR-124 augmented the migratory and invasive abilities in A549 and H1299 cells. The 3'-untranslated region of LHX2 transcript has also been identified to be a putative target of miR-124. Taken together, the results revealed that miR-124 may inhibit migration and invasion by repressing LHX2 expression in NSCLC cells. The findings of the present study suggested that overexpression of miR-124 or silencing of LHX2 may provide a therapeutic strategy for advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: LIM-homeobox 2; invasion; microRNA-124; migration; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-1238 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting LHX2 in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 7;6(22):19043-54. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4232. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26189214 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-99a is downregulated and promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer A549 and H1299 cells.Oncol Lett. 2015 Mar;9(3):1128-1134. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.2873. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25663868 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating autophagy activity via AMPK/ULK1 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Sep;16(3):2038-2045. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6370. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30186437 Free PMC article.
-
miR-4284 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells and is Associated with Postoperative Prognosis.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Jul 28;13:5865-5872. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S305379. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34349559 Free PMC article.
-
miR-204 suppresses non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) invasion and migration by targeting JAK2.Genet Mol Res. 2016 May 20;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15026415. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27323056
Cited by
-
LHX2 Enhances the Malignant Phenotype of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Upregulating the Expression of SERPINE2.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;13(8):1457. doi: 10.3390/genes13081457. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011368 Free PMC article.
-
Function of microRNA‑124 in the pathogenesis of cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Jan;64(1):6. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5594. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38038165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of LIMD2 promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):2073-2081. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10473. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423280 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Prognostic Signature of Transcription Factors for the Prediction in Patients With GBM.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 1;10:906. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00906. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31632439 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-124a Regulates Extracellular Vesicle Release by Targeting GTPase Rabs in Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 20;10:1454. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01454. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu Z, Zhao J, Zhang HT. JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2014;44:1643–1651. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
