Morphological and Functional Analyses of the Tight Junction in the Palatal Epithelium of Mouse
- PMID: 28928541
- PMCID: PMC5593814
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.17006
Morphological and Functional Analyses of the Tight Junction in the Palatal Epithelium of Mouse
Abstract
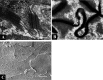
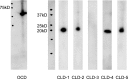
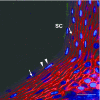
Tight junction (TJ) is one of the cell-cell junctions and known to have the barrier and fence functions between adjacent cells in both simple and stratified epithelia. We examined the distribution pattern, constitutive proteins, and permeability of TJ in the stratified squamous epithelium of the palatal mucosa of mice. Ultrastructural observations based on the ultrathin section and freeze-fracture methods revealed that poorly developed TJs are located at the upper layer of the stratum granulosum. The positive immunofluorescence of occludin (OCD), claudin (CLD)-1 and -4 were localized among the upper layer of the stratum granulosum showing a dot-like distribution pattern. And CLD-1 and -4 were localized among the stratum spinosum and the lower part of stratum granulosum additionally showed a positive reaction along the cell profiles. Western blotting of TJ constitutive proteins showed OCD, CLD-1, -2, -4, and -5 bands. The permeability test using biotin as a tracer revealed both the areas where biotin passed through beyond OCD positive points and the areas where biotin stopped at OCD positive points. These results show that poor TJs localize at the upper layer of the stratum granulosum of the palatal epithelium, and the TJs are leaky and include at least CLD-1 and -4.
Keywords: claudin; occludin; palatal epithelium; stratum granulosum; tight junction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tight junctions and compositionally related junctional structures in mammalian stratified epithelia and cell cultures derived therefrom.Eur J Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;81(8):419-35. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00270. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12234014
-
Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier: a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice.J Cell Biol. 2002 Mar 18;156(6):1099-111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200110122. Epub 2002 Mar 11. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11889141 Free PMC article.
-
Tight junction-related structures in the absence of a lumen: occludin, claudins and tight junction plaque proteins in densely packed cell formations of stratified epithelia and squamous cell carcinomas.Eur J Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;82(8):385-400. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00330. Eur J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14533737
-
A Review of a Breakdown in the Barrier: Tight Junction Dysfunction in Dental Diseases.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2024 Dec 30;16:513-531. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S492107. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2024. PMID: 39758089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming barriers in the study of tight junction functions: from occludin to claudin.Genes Cells. 1998 Sep;3(9):569-73. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1998.00212.x. Genes Cells. 1998. PMID: 9813107 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and Morphological Characterization of a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor ARHGEF9 in Mouse Tissues.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2018 Jun 26;51(3):119-128. doi: 10.1267/ahc.18009. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2018. PMID: 30083020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bizikova P., Linder K. E. and Olivry T. (2011) Immunomapping of desmosomal and nondesmosomal adhesion molecules in healthy canine footpad, haired skin and buccal mucosal epithelia: comparison with canine pemphigus foliaceus serum immunoglobulin G staining patterns. Vet. Dermatol. 22; 132–142. - PubMed
-
- Caputo R. and Peluchetti D. (1977) The junctions of normal human epidermis. A freeze-fracture study. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 61; 44–61. - PubMed
-
- Claude P. (1978) Morphological factors influencing transepithelial permeability: a model for the resistance of the zonula occludens. J. Membr. Biol. 39; 219–232. - PubMed
-
- Dos Reis P. P., Bharadwaj R. R., Machado J., Macmillan C., Pintilie M., Sukhai M. A., Perez-Ordonez B., Gullane P., Irish J. and Kamel-Reid S. (2008) Claudin 1 overexpression increases invasion and is associated with aggressive histological features in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 113; 3169–3180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

