Congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm: Atypical presentation
- PMID: 28928618
- PMCID: PMC5594943
- DOI: 10.4103/apc.APC_4_17
Congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm: Atypical presentation
Abstract
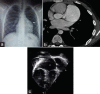
Congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm is a rare condition caused by dysplasia of the atrial muscles. We report a case of a 14-year-old boy, with a 5-month history of cough and in sinus rhythm. Transthoracic echocardiography and computerized tomographic angiography confirmed the aneurysm of the left atrial appendage which was resected through median sternotomy on cardiopulmonary bypass. This case is presented not only for its rarity but also for its atypical clinical presentation.
Keywords: Aneurysmectomy; congenital heart disease; left atrial appendage aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Left atrial appendage aneurysm: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Oct 6;8(19):4443-4449. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i19.4443. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33083403 Free PMC article.
-
Left atrial appendage aneurysm-a rare anomaly with an atypical presentation.Congenit Heart Dis. 2009 Nov-Dec;4(6):489-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0803.2009.00319.x. Congenit Heart Dis. 2009. PMID: 19925547
-
Congenital aneurysm of the left atrial appendage.Ann Thorac Surg. 2008 Jun;85(6):2139-40. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.12.064. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008. PMID: 18498847
-
Congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm: a case report and brief review of literature.Heart Lung Circ. 2009 Dec;18(6):412-6. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2008.10.015. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Heart Lung Circ. 2009. PMID: 19119072 Review.
-
[Giant congenital intrapericardial left atrial appendage aneurysm: about a case and review of the literature].Pan Afr Med J. 2016 Jul 12;24:225. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.24.225.10012. eCollection 2016. Pan Afr Med J. 2016. PMID: 27800080 Free PMC article. Review. French.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Giant Congenital Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm Presenting With Acute Massive Cerebral Infarction and Refractory Atrial Fibrillation: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 10;9:888825. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.888825. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35620516 Free PMC article.
-
Left atrial appendage aneurysm: a descriptive systematic review of 177 cases.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Nov 11;24(1):633. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04323-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39528946 Free PMC article.
-
Left atrial appendage aneurysm: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Oct 6;8(19):4443-4449. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i19.4443. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33083403 Free PMC article.
-
Left atrial appendage aneurysm in pediatrics: Case study and literature review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 10;10:1211619. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1211619. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37636313 Free PMC article.
-
The lethal fifth cardiac chamber: a rare autopsy case report of left atrial appendage aneurysm and review of literature.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025 Feb 7. doi: 10.1007/s12024-025-00963-3. Online ahead of print. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39918702
References
-
- Aryal MR, Hakim FA, Ghimire S, Ghimire S, Giri S, Pandit A, et al. Left atrial appendage aneurysm: A systematic review of 82 cases. Echocardiography. 2014;31:1312–8. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury UK, Seth S, Govindappa R, Jagia P, Malhotra P. Congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm: A case report and brief review of literature. Heart Lung Circ. 2009;18:412–6. - PubMed
-
- Van der Hauwaert LG, Dumoulin M, Daenen W, Stalpaert G. Aneurysm of the left atrial appendage. Clin Cardiol. 1979;2:49–51. - PubMed
-
- Kiaii B, Doll N, Kuehl M, Mohr FW. Minimal invasive endoscopic resection of a giant left atrial appendage aneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;77:1437–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

