Intrarenal Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: the Old and the New
- PMID: 28929450
- PMCID: PMC5913745
- DOI: 10.1007/s11906-017-0778-2
Intrarenal Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: the Old and the New
Abstract
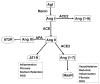
Purpose of review: The intrarenal renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS) is an independent paracrine hormonal system with an increasingly prominent role in hypertension and renal disease. Two enzyme components of this system are angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and more recently discovered ACE2. The purpose of this review is to describe recent discoveries regarding the roles of intrarenal ACE and ACE2 and their interaction.
Recent findings: Renal tubular ACE contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension. Additionally, the relative expression and activity of intrarenal ACE and ACE2 are central to promoting or inhibiting different renal pathologies including renovascular hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, and renal fibrosis. Renal ACE and ACE2 represent two opposing axes within the intrarenal RAS system whose interaction determines the progression of several common disease processes. While this relationship remains complex and incompletely understood, further investigations hold the potential for creating novel approaches to treating hypertension and kidney disease.
Keywords: ACE; ACE2; Hypertension; Kidney; RAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New insights and perspectives on intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: focus on intracrine/intracellular angiotensin II.Peptides. 2011 Jul;32(7):1551-65. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 21699940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrarenal alterations of the angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2/angiotensin 1-7 complex of the renin-angiotensin system do not alter the course of malignant hypertension in Cyp1a1-Ren-2 transgenic rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Apr;43(4):438-49. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12553. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26833491
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: possible role in hypertension and kidney disease.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2008 Feb;10(1):70-7. doi: 10.1007/s11906-008-0014-1. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2008. PMID: 18367030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: does it exist? Implications from a recent study in renal angiotensin-converting enzyme knockout mice.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Dec;28(12):2977-82. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft333. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23901049 Review.
-
ACE2 and vasoactive peptides: novel players in cardiovascular/renal remodeling and hypertension.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):217-37. doi: 10.1177/1753944715597623. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26275770 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin and Alternative Pathways in Diabetic Nephropathy - A Review.Rev Diabet Stud. 2021 Spring;17(1):1-10. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2021.17.1. Epub 2021 May 10. Rev Diabet Stud. 2021. PMID: 34289001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Previous and Current Evidence-Based Therapeutic Approaches.Adv Ther. 2022 Aug;39(8):3488-3500. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02223-0. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35751762 Review.
-
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;12:754239. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.754239. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34790127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive significance of glomerular insulin receptor substrate-1 in patients with diabetic kidney disease.Metabol Open. 2023 Mar 22;18:100240. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2023.100240. eCollection 2023 Jun. Metabol Open. 2023. PMID: 37025096 Free PMC article.
-
Deep transcriptomic profiling of Dahl salt-sensitive rat kidneys with mutant form of Resp18.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Oct 1;572:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.071. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34340197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rohrwasser A, Morgan T, Dillon HF, Zhao L, Callaway CW, Hillas E, et al. Elements of a paracrine tubular renin-angiotensin system along the entire nephron. Hypertension. 1999;34:1265–74. - PubMed
-
- Yang T, Xu C. Physiology and pathophysiology of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: an update. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:1040–9. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016070734A recent review on the function and regulation of the intrarenal RAS in contrast with systemic RAS. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsusaka T, Niimura F, Shimizu A, Pastan I, Saito A, Kobori H, et al. Liver angiotensinogen is the primary source of renal angiotensin II. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1181–9. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011121159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casarini DE, Boim MA, Stella RC, Krieger-Azzolini MH, Krieger JE, Schor N. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity in tubular fluid along the rat nephron. Am J Phys. 1997;272:F405–9. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama A, Seth DM, Navar LG. Renal interstitial fluid angiotensin I and angiotensin II concentrations during local angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2207–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

