GC-MS Analysis and Preliminary Antimicrobial Activity of Albizia adianthifolia (Schumach) and Pterocarpus angolensis (DC)
- PMID: 28930113
- PMCID: PMC5456228
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines3010003
GC-MS Analysis and Preliminary Antimicrobial Activity of Albizia adianthifolia (Schumach) and Pterocarpus angolensis (DC)
Abstract
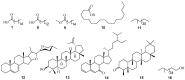
The non-polar components of two leguminoceae species Albizia adianthifolia (Schumach), and Pterocarpus angolensis (DC) were investigated. GC-MS analysis of the crude n-hexane and chloroform extracts together with several chromatographic separation techniques led to the identification and characterization (using NMR) of sixteen known compounds from the heartwood and stem bark of Albizia adianthifolia and Pterocarpus angolensis respectively. These constituents include, n-hexadecanoic acid (palmitic acid) 1, oleic acid 2, chondrillasterol 3, stigmasterol 4, 24S 5α-stigmast-7-en-3β-ol 5, 9,12-octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)-, methyl ester 6, trans-13-octadecanoic acid, methyl ester 7, tetradecanoic acid 8, hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester 9, octadecanoic acid 10, tetratriacontane 11, 7-dehydrodiosgenin 12, lupeol 13, stigmasta-3,5-diene-7-one 14, friedelan-3-one (friedelin) 15, and 1-octacosanol 16. Using agar over lay method, the preliminary antimicrobial assay for the extracts was carried out against bacterial (E. coli, P. aeruginosa, B. subtilis, S. aueus) and a fungus/yeast (C. albicans) strains. The n-hexane and chloroform extracts of A. adianthifolia showed the best activity against E. coli with minimum inhibition quantity (MIQ) of 1 µg each while the remaining exhibited moderate-to-weak activity against the test microorganisms.
Keywords: A. adianthifolia; GC-MS; NMR; P. angolensis; antimicrobial activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemicals from Pterocarpus angolensis DC and Their Cytotoxic Activities against Breast Cancer Cells.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;13(2):301. doi: 10.3390/plants13020301. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276759 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial effects of Alchornea cordifolia (Schumach. and Thonn.) Müll. Arg extracts and compounds on gastrointestinal, skin, respiratory and urinary tract pathogens.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.043. Epub 2015 Dec 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26724423
-
Crude extracts of, and purified compounds from, Pterocarpus angolensis, and the essential oil of Lippia javanica: their in-vitro cytotoxicities and activities against selected bacteria and Entamoeba histolytica.Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2009 Jul;103(5):427-39. doi: 10.1179/136485909X435111. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19583913
-
Antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of leaf extract and fractions of Albizia adianthifolia (Schumach) W.F. Wright.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 1;28(2):143-148. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2015-0054. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27658138
-
In silico anti-SARS-CoV-2, antiplasmodial, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of crude extracts and homopterocarpin from heartwood of Pterocarpus macrocarpus Kurz.Heliyon. 2023 Feb;9(2):e13644. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13644. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36789389 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Estimation of drug-likeness properties of GC-MS separated bioactive compounds in rare medicinal Pleione maculata using molecular docking technique and SwissADME in silico tools.Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinform. 2021;10(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s13721-020-00276-1. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33643765 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the biomarkers in anti-MRSA fractions of soil Streptomycetes by multivariate analysis.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 May 10;118(6):77. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02087-8. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40347296
-
Heliotropium ramosissimum metabolic profiling, in silico and in vitro evaluation with potent selective cytotoxicity against colorectal carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 22;12(1):12539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16552-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35869153 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antibacterial activity of medicinal plants against biofilm-forming methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: efficacy of Moringa stenopetala and Rosmarinus officinalis extracts.Heliyon. 2020 Jan 27;6(1):e03303. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03303. eCollection 2020 Jan. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32051871 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory effect of some natural bioactive compounds against SARS-CoV-2 main protease: insights from molecular docking analysis and molecular dynamic simulation.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2020;55(11):1373-1386. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2020.1826192. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2020. PMID: 32998618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delamare A.P.L., Moschen-Pistorello I.T., Artico L., Atti-Serafini L., Echeverrigaray S. Antibacterial activity of the essential oils of Salvia officinalis L. and Salvia triloba L. cultivated in South Brazil. Food Chem. 2007;100:603–608. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.09.078. - DOI
-
- Lawal I.O., Uzokwe N.E., Igboanugo A.B.I., Adio A.F., Awosan E.A., Nwogwugwu J.O., Faloye B., Olatunji B.P., Adesoga A.A. Ethno-medicinal information on collation and identification of some medicinal plants in research institutes of South-west Nigeria. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010;4:1–7.
-
- Rojo J.P. Pterocarpus (Leguminoseae-Papillinaceae) Revised for the World. Verlag Von J Cramer; Lehre, Germany: 1972.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous