Human Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells Are Defined by Core Transcriptional and Functional Signatures in Lymphoid and Mucosal Sites
- PMID: 28930685
- PMCID: PMC5646692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.078
Human Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells Are Defined by Core Transcriptional and Functional Signatures in Lymphoid and Mucosal Sites
Abstract
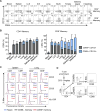
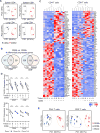
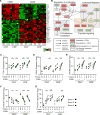
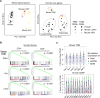
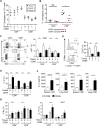
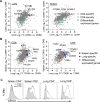
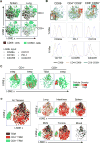
Tissue-resident memory T cells (TRMs) in mice mediate optimal protective immunity to infection and vaccination, while in humans, the existence and properties of TRMs remain unclear. Here, we use a unique human tissue resource to determine whether human tissue memory T cells constitute a distinct subset in diverse mucosal and lymphoid tissues. We identify a core transcriptional profile within the CD69+ subset of memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in lung and spleen that is distinct from that of CD69- TEM cells in tissues and circulation and defines human TRMs based on homology to the transcriptional profile of mouse CD8+ TRMs. Human TRMs in diverse sites exhibit increased expression of adhesion and inhibitory molecules, produce both pro-inflammatory and regulatory cytokines, and have reduced turnover compared with circulating TEM, suggesting unique adaptations for in situ immunity. Together, our results provide a unifying signature for human TRM and a blueprint for designing tissue-targeted immunotherapies.
Keywords: RNA-seq; human immunology; memory T cells; mucosal immunity.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

