Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Death in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 28930918
- PMCID: PMC5811234
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000993
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Death in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
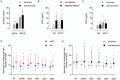
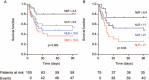
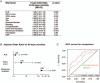
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is an inflammation score recognized as associated with outcome. Although inflammation has been shown to correlate with the development of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), we sought to investigate the role of NLR in predicting 90-day mortality in cirrhotic patients experiencing ACLF. We performed a retrospective cohort study involving a total of 108 consecutive cirrhotic patients admitted in the intensive care unit (ICU). NLR, clinical and biological data were recorded. Of the total, 75 patients had ACLF. The 90-day mortality rate was 53%. ACLF patients displayed higher NLR values in comparison with cirrhotic patients without ACLF throughout the ICU stay. NLR proved more elevated in nonsurvivors ACLF patients, with mortality correlating with increasing quartiles of NLR. On multivariable Cox regression analysis, NLR was found to be a predictor of mortality along with the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score and mechanical ventilation requirement. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score was not predictive of 90-days mortality. Performance analysis revealed an area under curve of 0.71 [95% confidence interval: 0.59-0.82] regarding NLR capacity to predict 90-days mortality. When including NLR, SOFA score, and mechanical ventilation requirement into the final model, the area under curve was significantly higher (0.81 [95% confidence interval: 0.72-0.91]).These findings suggest that NLR is associated with mortality in ACLF patients admitted to the ICU. Combining NLR, SOFA score, and the need for mechanical ventilation could be a useful prognostic tool to identify ACLF patients at a higher risk of mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gibson PH, Croal BL, Cuthbertson BH, Small GR, Ifezulike AI, Gibson G, Jeffrey RR, Buchan KG, El-Shafei H, Hillis GS. Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and outcome from coronary artery bypass grafting. Am Heart J 2007; 154 5:995–1002. - PubMed
-
- Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocaña A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G, Knox JJ, Tran B, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2014; 106 6:dju124. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Lou Y, Chen Y, Yang J. Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Int J Clin Pract 2014; 68 8:1034–1040. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

