Whole-genome sequencing of mutants with increased resistance against the two-peptide bacteriocin plantaricin JK reveals a putative receptor and potential docking site
- PMID: 28931059
- PMCID: PMC5607208
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185279
Whole-genome sequencing of mutants with increased resistance against the two-peptide bacteriocin plantaricin JK reveals a putative receptor and potential docking site
Abstract
By whole-genome sequencing of resistant mutants, a putative receptor for plantaricin JK, a two-peptide bacteriocin produced by some Lactobacillus plantarum strains, was identified in Lactobacillus plantarum NCFB 965 and Weissella viridescens NCFB 1655. The receptors of the two species had 66% identical amino acid sequences and belong to the amino acid-polyamine-organocation (APC) transporter protein family. The resistant mutants contained point mutations in the protein-encoding gene resulting in either premature stop codons, leading to truncated versions of the protein, or single amino acid substitutions. The secondary structure of the W. viridescens protein was predicted to contain 12 transmembrane (TM) helices, a core structure shared by most members of the APC protein family. The single amino acid substitutions that resulted in resistant strains were located in a confined region of the protein that consists of TM helix 10, which is predicted to be part of an inner membrane pore, and an extracellular loop between TM helix 11 and 12. By use of template-based modeling a 3D structure model of the protein was obtained, which visualizes this mutational hotspot region and further strengthen the hypothesis that it represents a docking site for plantaricin JK.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

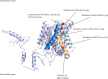
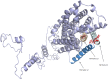
References
-
- Kjos M, Borrero J, Opsata M, Birri DJ, Holo H, Cintas LM, et al. Target recognition, resistance, immunity and genome mining of class II bacteriocins from Gram-positive bacteria. Microbiology. 2011;157(Pt 12):3256–67. Epub 2011/10/08. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.052571-0 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramnath M, Beukes M, Tamura K, Hastings JW. Absence of a putative mannose-specific phosphotransferase system enzyme IIAB component in a leucocin A-resistant strain of Listeria monocytogenes, as shown by two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66(7):3098–101. Epub 2000/07/06. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC92118. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Héchard Y, Sahl H-G. Mode of action of modified and unmodified bacteriocins from Gram-positive bacteria. Biochimie. 2002;84(5–6):545–57. Epub 2002/11/09. . - PubMed
-
- Diep DB, Skaugen M, Salehian Z, Holo H, Nes IF. Common mechanisms of target cell recognition and immunity for class II bacteriocins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(7):2384–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608775104 ISI:000244438500062. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gabrielsen C, Brede DA, Hernandez PE, Nes IF, Diep DB. The maltose ABC transporter in Lactococcus lactis facilitates high-level sensitivity to the circular bacteriocin garvicin ML. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(6):2908–15. Epub 2012/03/14. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00314-12 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3370726. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

