Influence of Quercetin in the Temporal Regulation of Redox Homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 28931163
- PMCID: PMC5605229
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/iex040
Influence of Quercetin in the Temporal Regulation of Redox Homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
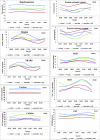
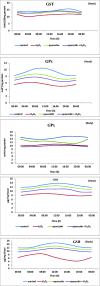
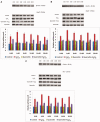
Numerous biological processes are governed by the biological clock. Studies using Drosophila melanogaster (L.) are valuable that could be of importance for their effective applications on rodent studies. In this study, the beneficial role of quercetin (a flavonoid) on H2O2 induced stress in D. melanogaster was investigated. D. melanogaster flies were divided into four groups (group I - control, group II - H2O2 (acute exposure), group III - quercetin, and group IV - quercetin + H2O2 treated). Negative geotaxis assay, oxidative stress indicators (protein carbonyls, thiobarbituric reactive substances [TBARS]), and antioxidants (superoxide dismutase [SOD], catalase [CAT], glutathione-S-transferase [GST], glutathione peroxidase, and reduced glutathione [GSH]) were measured at 4 h intervals over 24 h and temporal expression of heat shock protein-70 (Hsp70), Upd1 (homolog of IL-6 in Drosophila), and nitric oxide synthase (Nos) was analyzed by Western blotting. Groups II and IV showed altered biochemical rhythms (compared with controls). Decreased mesor values of negative geotaxis, SOD, CAT, GST, and GSH were noticed in H2O2, increased mesor of oxidative stress indicators (TBARS and protein carbonyl content) and a reversibility of the rhythmic characteristics were conspicuous after quercetin treatment. The expression levels of Hsp70, Upd1, and Nos were noticeably maximum at 04:00. Significant elevation of expression by H2O2 was nearly normalized by quercetin treatment. The possible mechanism by which quercetin modulates oxidant-antioxidant imbalance under oxidative stress could be ascribed to the modulation of the rhythmic properties. Our results will be helpful to understand the molecular interlink between circadian rhythm and oxidative stress mechanism.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; circadian; oxidative stress; quercetin.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Entomological Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Bacopa monnieri in the temporal regulation of oxidative stress in clock mutant (cryb) of Drosophila melanogaster.J Insect Physiol. 2014 Jun;65:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Apr 26. J Insect Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24780191
-
Quercetin modulates OTA-induced oxidative stress and redox signalling in HepG2 cells - up regulation of Nrf2 expression and down regulation of NF-κB and COX-2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1840(1):681-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24161694
-
Ameliorative effects of gallic acid, quercetin and limonene on urethane-induced genotoxicity and oxidative stress in Drosophila melanogaster.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2017 May;27(4):286-292. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2016.1278294. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2017. PMID: 28043195
-
The multifaceted role of quercetin derived from its mitochondrial mechanism.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Aug;479(8):1985-1997. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04833-w. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37656383 Review.
-
Redox stress shortens lifespan through suppression of respiratory complex I in flies with mitonuclear incompatibilities.Exp Gerontol. 2023 May;175:112158. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112158. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Exp Gerontol. 2023. PMID: 36965604 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-obesity effects of Erythrina abyssinica stem bark extract in flies exposed to a high fat diet.Heliyon. 2022 Jul 6;8(7):e09886. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09886. eCollection 2022 Jul. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35847607 Free PMC article.
-
Senolytic and senomorphic secondary metabolites as therapeutic agents in Drosophila melanogaster models of Parkinson's disease.Front Neurol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1271941. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1271941. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37840914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-(2'-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-propylpentanamide (OH-VPA), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces the release of nuclear HMGB1 and modifies ROS levels in HeLa cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Sep 7;9(70):33368-33381. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26077. eCollection 2018 Sep 7. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30279967 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Sleep-Improvement Effects of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni in Drosophila melanogaster and Targeted Screening to Identify Its Active Components and Mechanism.Foods. 2021 Apr 17;10(4):883. doi: 10.3390/foods10040883. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33920660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aebi H. 1984. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 105: 121–126. - PubMed
-
- Ahamed M., Posgai R., Gorey T. J., Nielsen M., Hussain S. M., Rowe J. J.. 2010. Silver nanoparticles induced heat shock protein 70, oxidative stress and apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 242: 263–269. - PubMed
-
- Avanesian A., Semnani S., Jafari M.. 2009. Can Drosophila melanogaster represent a model system for the detection of reproductive adverse drug reactions? Drug Discov. Today. 14: 761–766. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

