PIBAS FedSPARQL: a web-based platform for integration and exploration of bioinformatics datasets
- PMID: 28931422
- PMCID: PMC5607505
- DOI: 10.1186/s13326-017-0151-z
PIBAS FedSPARQL: a web-based platform for integration and exploration of bioinformatics datasets
Abstract
Background: There are a huge variety of data sources relevant to chemical, biological and pharmacological research, but these data sources are highly siloed and cannot be queried together in a straightforward way. Semantic technologies offer the ability to create links and mappings across datasets and manage them as a single, linked network so that searching can be carried out across datasets, independently of the source. We have developed an application called PIBAS FedSPARQL that uses semantic technologies to allow researchers to carry out such searching across a vast array of data sources.
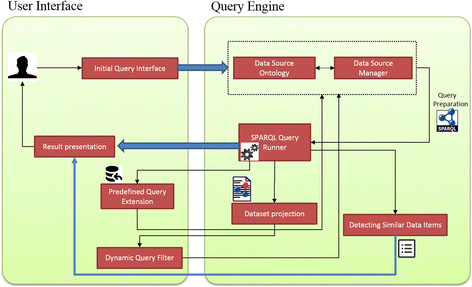
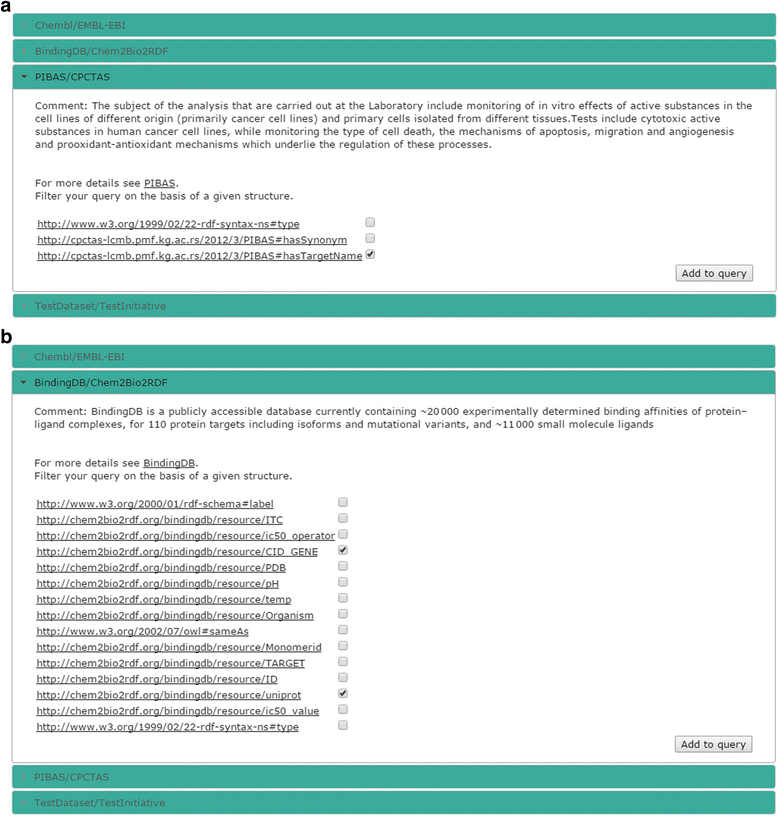
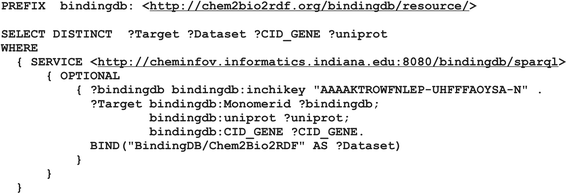
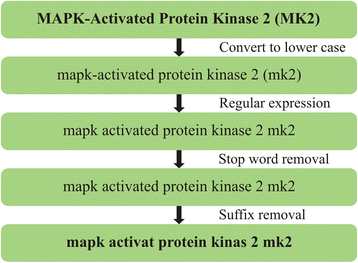
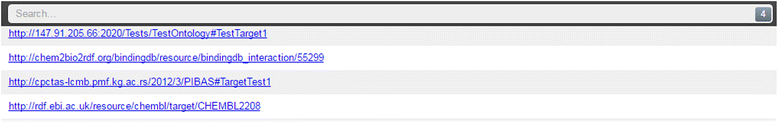
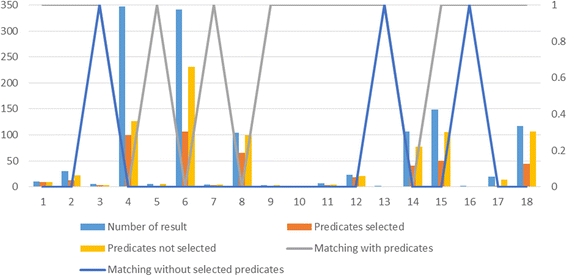
Results: PIBAS FedSPARQL is a web-based query builder and result set visualizer of bioinformatics data. As an advanced feature, our system can detect similar data items identified by different Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs), using a text-mining algorithm based on the processing of named entities to be used in Vector Space Model and Cosine Similarity Measures. According to our knowledge, PIBAS FedSPARQL was unique among the systems that we found in that it allows detecting of similar data items. As a query builder, our system allows researchers to intuitively construct and run Federated SPARQL queries across multiple data sources, including global initiatives, such as Bio2RDF, Chem2Bio2RDF, EMBL-EBI, and one local initiative called CPCTAS, as well as additional user-specified data source. From the input topic, subtopic, template and keyword, a corresponding initial Federated SPARQL query is created and executed. Based on the data obtained, end users have the ability to choose the most appropriate data sources in their area of interest and exploit their Resource Description Framework (RDF) structure, which allows users to select certain properties of data to enhance query results.
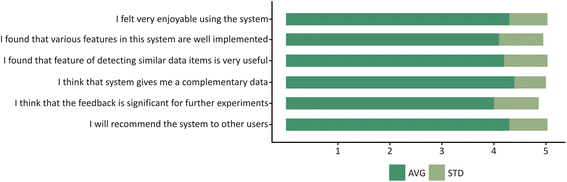
Conclusions: The developed system is flexible and allows intuitive creation and execution of queries for an extensive range of bioinformatics topics. Also, the novel "similar data items detection" algorithm can be particularly useful for suggesting new data sources and cost optimization for new experiments. PIBAS FedSPARQL can be expanded with new topics, subtopics and templates on demand, rendering information retrieval more robust.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Data integration; Data mining and information retrieval; Federated SPARQL query; Ontologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
MDJP is a Research Associate and PhD student of computer science at the Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Faculty of Science, University of Kragujevac, Serbia. She is currently employed as a software developer at an Austrian company that is supported by the Graz University of Technology. VC is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Faculty of Science, University of Kragujevac, Serbia. JY is a research scientist at the School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University and Translational Informatics Division, School of Medicine, University of New Mexico focused on bimolecular and biomedical data science. MZ is a Research Associate at the Department of Biology and Ecology, Faculty of Science, University of Kragujevac, Serbia. DW is an Associate Professor at Indiana University School of Informatics and Computing, and leads the Integrative Data Science Laboratory. This group created one of the original semantic data sources used in this work (Chem2Bio2RDF).
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
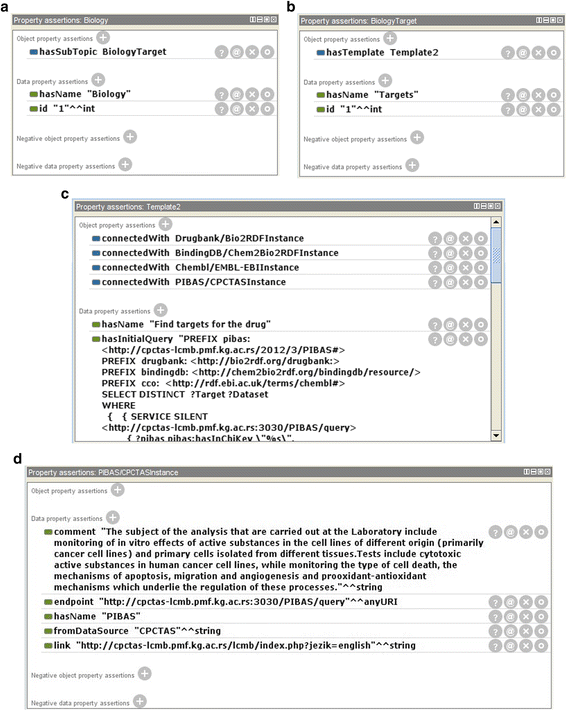

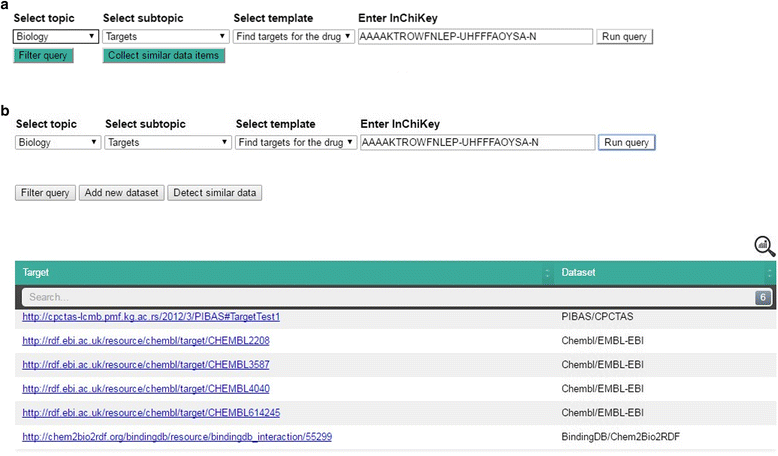
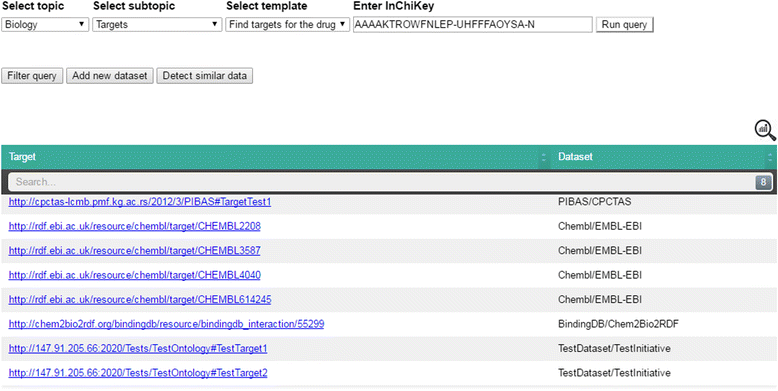
 icon in the top-right corner of the table shows statistical information about the retrieved data, including data source name, initiative name and the number of obtained data items per data source
icon in the top-right corner of the table shows statistical information about the retrieved data, including data source name, initiative name and the number of obtained data items per data source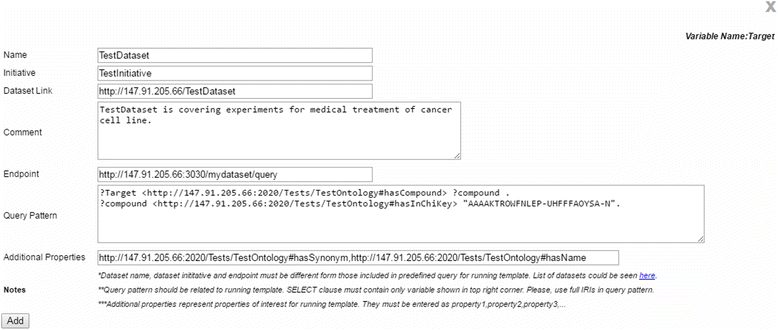


Similar articles
-
BioFed: federated query processing over life sciences linked open data.J Biomed Semantics. 2017 Mar 15;8(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13326-017-0118-0. J Biomed Semantics. 2017. PMID: 28298238 Free PMC article.
-
A journey to Semantic Web query federation in the life sciences.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 1;10 Suppl 10(Suppl 10):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S10-S10. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19796394 Free PMC article.
-
Chem2Bio2RDF: a semantic framework for linking and data mining chemogenomic and systems chemical biology data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 May 17;11:255. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-255. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20478034 Free PMC article.
-
LinkHub: a Semantic Web system that facilitates cross-database queries and information retrieval in proteomics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 May 9;8 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S3-S5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17493288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Techniques for optimization of queries on integrated biological resources.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2004 Jun;2(2):375-411. doi: 10.1142/s0219720004000648. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2004. PMID: 15297988 Review.
Cited by
-
Enabling semantic queries across federated bioinformatics databases.Database (Oxford). 2019 Jan 1;2019:baz106. doi: 10.1093/database/baz106. Database (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 31697362 Free PMC article.
-
Semantic Data Visualisation for Biomedical Database Catalogues.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;10(11):2287. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10112287. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masseroli M, Mons B, Bongcam-Rudloff E, Ceri S, Kel A, Rechenmann F, Lisacek F, Romano P. Integrated bio-search: challenges and trends for the integration, search and comprehensive processing of biological information. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15(Suppl 1):S2. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-15-S1-S2. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stephens S, LaVigna D, DiLascio M, Luciano J. Aggregation of bioinformatics data using Semantic Web technology. Web Semantics: Science, services and agents on the world wide web. 2006 Sep 30; 4(3):216–221.
-
- CPCTAS-LCMB, Faculty of Science, University of Kragujevac, Serbia, http://cpctas-lcmb.pmf.kg.ac.rs/lcmb/
-
- Cvjetkovic V, Djokic M, Arsic B, Curcic M. The ontology supported intelligent system for experiment search in the scientific research center. Kragujevac Journal of Science. 2014;36:95–110. doi: 10.5937/KgJSci1436095C. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

