Effects of whole body vibration exercise on neuromuscular function for individuals with knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 28931439
- PMCID: PMC5607567
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2170-6
Effects of whole body vibration exercise on neuromuscular function for individuals with knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a leading cause of public disability. Neuromuscular function contributes to the development and/or progression of KOA. Whole body vibration (WBV) exercise improve the neuromuscular function of patients with neurological disorders and even that of older patients with limited exercise options. Therefore, WBV exercise may offer an efficient and alternative treatment for individuals with KOA. However, the effects of WBV training on the neuromuscular function of individuals with KOA remain unclear. Therefore, this study attempts to investigate the effect of a 12-week WBV exercise on the neuromuscular function of individuals with KOA.
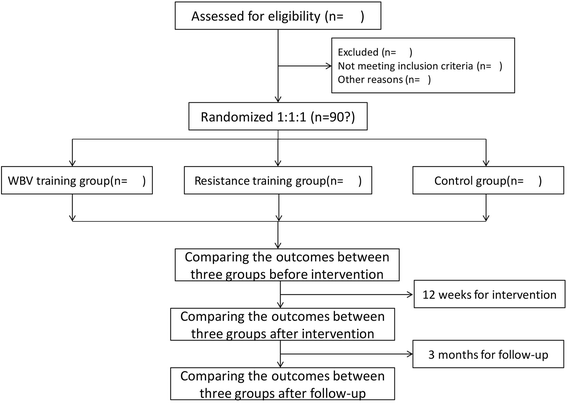
Methods/design: We will conduct a prospective, single-blind randomized controlled trial on 180 KOA patients. Participants will be randomly assigned to the WBV exercise, lower extremity resistance training, and health education groups. The WBV exercise group will participate in a 12-week WBV training. The lower extremity resistance training group will undergo a 12-week lower extremity resistance training of both lower limbs. The control group will receive health education for 12 weeks. After the intervention, the participants will be followed up for 3 months with no active intervention. Primary outcome measures will include anthropometric measurements, gait analysis during walking and stair climbing, muscle strength test of the knee and ankle, proprioception test of the knee and ankle, and neuromuscular response of the leg muscles. Secondary outcome measures will include self-reported pain and physical functional capacity, and physical performance measures. Furthermore, adverse events will be recorded and analyzed. If any participant withdraws from the trial, intention-to-treat analysis will be performed.
Discussion: Important features of this trial mainly include intervention setting, outcome measure selection, and study duration. This study is intended for estimating the effect of WBV intervention on neuromuscular control outcomes. Study results may provide evidence to support the beneficial effects of WBV exercise on the physical performance and neuromuscular control of individuals with KOA to fill the research gap on the efficacy of WBV.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ID: ChiCTR-IOR-16009234 . Registered on 21 September 2016.
Keywords: Knee osteoarthritis; Neuromuscular function; Randomized controlled trial; Strength training; Whole body vibration.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Shanghai University of Sport (Ref. No.: 2016-016). Informed consent will be obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Xu L, Nevitt MC, Aliabadi P, Yu W, Qin M, et al. Comparison of the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis between the elderly Chinese population in Beijing and whites in the United States: The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2065–71. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2065::AID-ART356>3.0.CO;2-Z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Department of Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion . Chronic rheumatic conditions. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous