A Cross Talk between Neuronal Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Astrocytic uPA Receptor (uPAR) Promotes Astrocytic Activation and Synaptic Recovery in the Ischemic Brain
- PMID: 28931568
- PMCID: PMC5656992
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1630-17.2017
A Cross Talk between Neuronal Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Astrocytic uPA Receptor (uPAR) Promotes Astrocytic Activation and Synaptic Recovery in the Ischemic Brain
Abstract
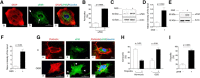
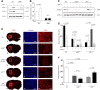
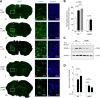
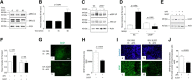
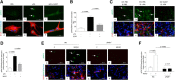
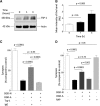
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is a serine proteinase that, upon binding to its receptor (uPAR), catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen into plasmin on the cell surface. Our previous studies indicate that uPA and uPAR expression increase in the ischemic brain during the recovery phase from an acute ischemic injury and that uPA binding to uPAR promotes neurological recovery after an acute ischemic stroke. Here, we used male mice genetically deficient on either uPA (uPA-/-) or uPAR (uPAR-/-) or with a four-amino acid substitution into the growth factor domain of uPA that abrogates its binding to uPAR (PlatGFDhu/GFDhu) to investigate the mechanism whereby uPA promotes neurorepair in the ischemic brain. We found that neurons release uPA and astrocytes recruit uPAR to their plasma membrane during the recovery phase from a hypoxic injury and that binding of neuronal uPA to astrocytic uPAR induces astrocytic activation by a mechanism that does not require plasmin generation, but instead is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2)-regulated phosphorylation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). We report that uPA/uPAR binding is necessary and sufficient to induce astrocytic activation in the ischemic brain and that astrocytes activated by neuronal uPA promote synaptic recovery in neurons that have suffered an acute hypoxic injury via a mechanism mediated by astrocytic thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) and synaptic low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1). In summary, we show that uPA/uPAR-induced astrocytic activation mediates a cross talk between astrocytes and injured neurons that promotes synaptic recovery in the ischemic brain.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT To date, there is no therapeutic strategy to promote synaptic recovery in the injured brain. Here, we show that neurons release urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and astrocytes recruit the uPA receptor (uPAR) to their plasma membrane during the recovery phase from a hypoxic injury. We found that binding of neuronal uPA to astrocytic uPAR promotes astrocytic activation and that astrocytes activated by uPA-uPAR binding promote synaptic recovery in neurons that have suffered a hypoxic injury by a mechanism that does not require plasmin generation, but instead is mediated by ERK1/2-regulated STAT3 phosphorylation, astrocytic thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) and synaptic low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1). Our work unveils a new biological function for uPA-uPAR as mediator of a neuron-astrocyte cross talk that promotes synaptic recovery in the ischemic brain.
Keywords: astrogliosis; neurorepair; plasmin; recovery; urokinase-type plasminogen activator.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/3710311-13$15.00/0.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) protects the tripartite synapse in the ischemic brain via ezrin-mediated formation of peripheral astrocytic processes.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Nov;39(11):2157-2171. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18783653. Epub 2018 Jun 12. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 29890880 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) promotes ezrin-mediated reorganization of the synaptic cytoskeleton in the ischemic brain.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 15;293(24):9234-9247. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002534. Epub 2018 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29720403 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator promotes dendritic spine recovery and improves neurological outcome following ischemic stroke.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 22;34(43):14219-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5309-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25339736 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is a modulator of synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system: implications for neurorepair in the ischemic brain.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Apr;15(4):620-624. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.266904. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31638083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Plasminogen Activation System Promotes Neurorepair in the Ischemic Brain.Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(9):953-959. doi: 10.2174/1389450120666181211144550. Curr Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30539695 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control of complex behavior by astrocytes and microglia.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jun;137:104651. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104651. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35367512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane Associated RNA-Containing Vesicles Regulate Cortical Astrocytic Microdomain Calcium Transients in Awake Ischemic Stroke Mice.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(46):e2404391. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404391. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39444078 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinolytic Serine Proteases, Therapeutic Serpins and Inflammation: Fire Dancers and Firestorms.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 25;8:648947. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.648947. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33869309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Effect of LPS on the Proliferation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells through the Notch Signaling Pathway in Intrauterine Infection-induced Rats.Curr Med Sci. 2018 Oct;38(5):840-846. doi: 10.1007/s11596-018-1951-9. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Curr Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30341518
-
The uPA/uPAR system in astrocytic wound healing.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Nov;17(11):2404-2406. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.338991. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35535878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
